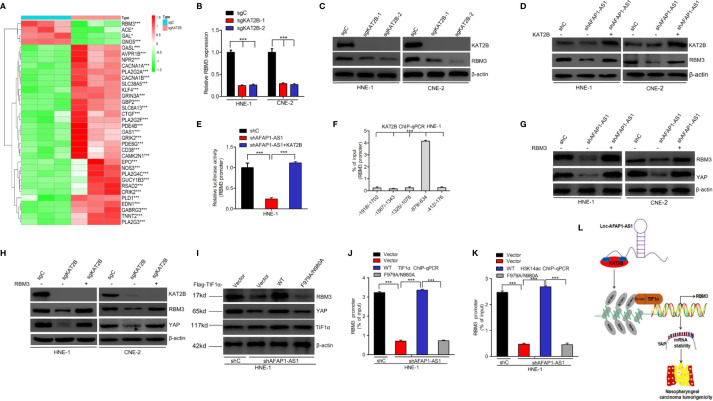
Figure 8.
TIF1α/H3K14ac complex activation of RBM3 transcription is required for AFAP1-AS1–modulation of YAP stability. (A) Heatmaps of RNA-Seq data for RBM3 and its target genes in HNE-1 cells with KAT2B sgRNA or a control sgRNA. (B, C), KAT2B knockout inhibits RBM3 mRNA (B) and protein (C) expression. (D, E) Effects of KAT2B overexpression on AFAP1-AS1 knockdown-suppressed RBM3 protein expression (D) and RBM3 promoter activity (E). (F) ChIP-qPCR assay of KAT2B binding at different loci within the RBM3 promoter. IgG is used as a control. (G) RBM3 overexpression rescues AFAP1-AS1 knockdown-mediated suppression of YAP. (H) Effects of RBM3 overexpression on KAT2B knockout-mediated YAP repression. (I) TIF1α wild-type, but not the F979A/N980A mutant, restores AFAP1-AS1 knockdown-suppressed YAP expression in HNE-1 cells. (J, K) Effect of TIF1α wild-type and F979A/N980A mutant overexpression on AFAP1-AS1 knockdown-suppressed TIF1α binding (J), H3K14ac (K), and the RBM3 promoter. (L) A working model for AFAP1-AS1–mediated NPC tumorigenicity. Error bars represent the standard deviation. *P < 0.05. ***P < 0.001.The data represent three independent experiment.