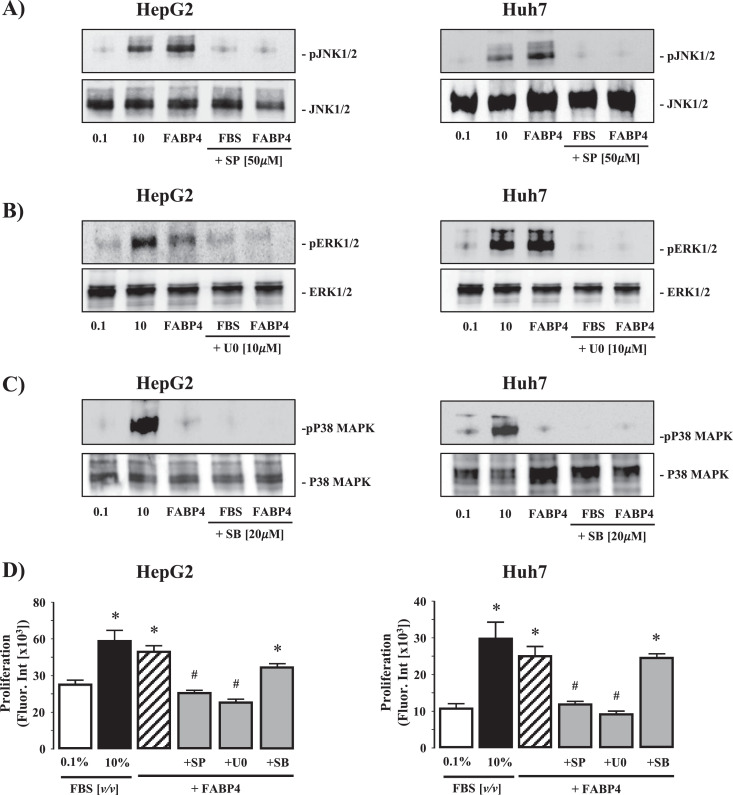
Fig. 5.
Intracellular signaling pathways involved in rhFABP4-stimulated hepatoma cell proliferation and migration in vitro. (A) Representative Western blot analysis of phosphorylated/total JNK1/2 (pJNK1/2 - JNK1/2) in HepG2 and HuH7 HCC cells following exposure to 0.1 or 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum (FBS), rhFABP4 (200 ng/mL), or 10% (v/v) FBS/rhFABP4 in the presence of SP 600,125 [SP; JNK inhibitor] (50 μM). (B) Phosphorylated/total ERK1/2 (pERK 1/2 - ERK 1/2) in HepG2 and HuH7 HCC cells following exposure to FBS, rhFABP4 (200 ng/mL), or FBS/rhFABP4 in the presence of U0126 [U0; ERK1/2 inhibitor] (10 μM). (C) Phosphorylated/total p38 mitogen-activate protein kinase (pp38MAPK - p38MAPK) in HepG2 and HuH7 HCC cells following exposure to FBS, rhFABP4 (100 ng/mL), or FBS/rhFABP4 in the presence of SB 203,589 [SB; p38MAPK inhibitor] (20 μM). D) HepG2 and HuH7 cells were pretreated with SB, U0, or SP for 60 min prior to exposure to exogenous rhFABP4 (200 ng/mL; 24 h) and assayed for proliferation. Negative and positive controls were 0.1% [v/v] and 10% [v/v] FBS respectively. *P<0.05 versus 0.1% [v/v] FBS, #P<0.05 versus rhFABP4, N = 4.