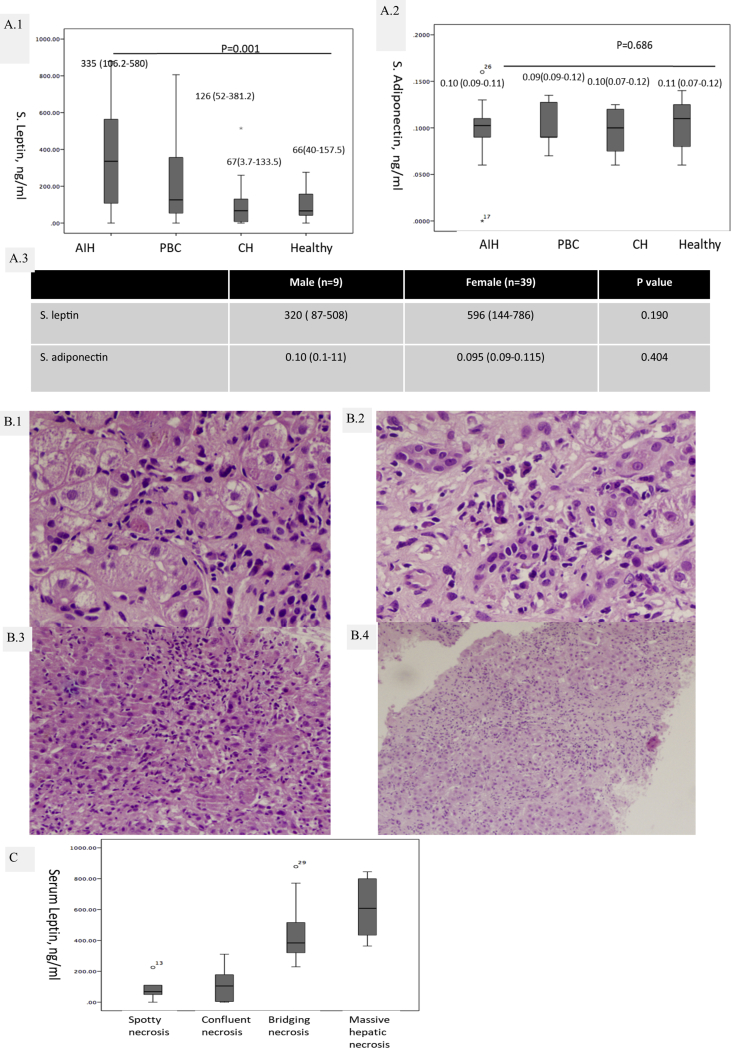
Figure 1.
A.1): levels of serum leptin; (A.2) Serum adiponectin and in autoimmune hepatitis (AIH), primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), chronic hepatitis (CH) and in healthy controls (HCs); (A.3) Comparison of serum leptin and adiponectin in AIH based on gender. Representative photomicrographs of (B.1) Spotty necrosis; (B.2) Confluent necrosis; (B.3) Bridging necrosis; (B.4) Massive hepatic necrosis in AIH [all H&E, 200×] and (C) distribution of serum leptin based on necrosis.