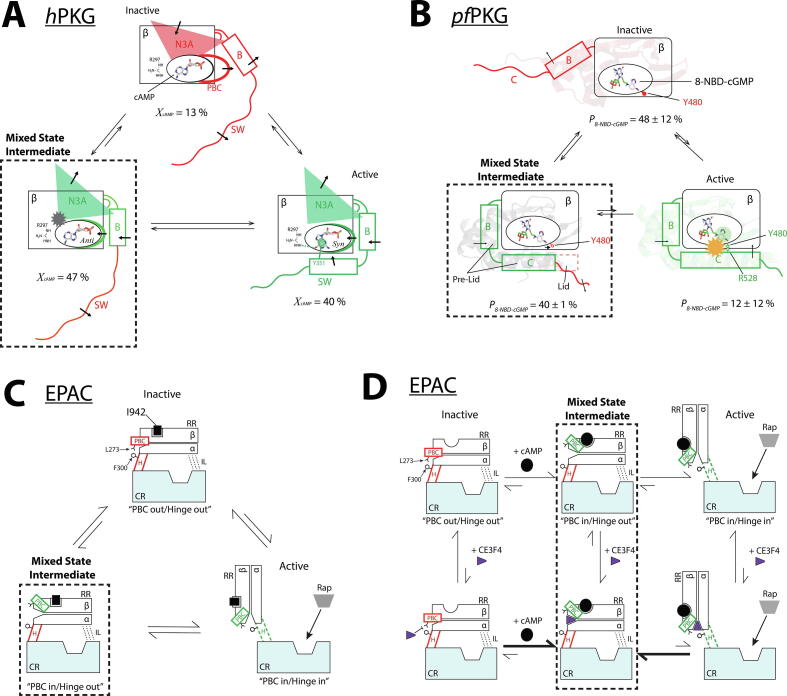
Fig. 2.
Sampling mixed intermediate states of isolated CBDs enables partial agonists to maximize inhibition without significantly compromising affinities. (A) CBD-B of human PKG bound to cAMP samples inactive and active conformers as well as an intermediate state (dashed box), where only its C-terminal switch helix (SW) is disengaged and dynamic [12]. The figure was reproduced with permission and was originally published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. VanSchouwen B, Selvaratnam R, Giri R, Lorenz R, Herberg FW, Kim C, et al. Mechanism of cAMP Partial Agonism in Protein Kinase G (PKG). J. Biol. Chem. 2015; 290:28631–38641. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. (B) Plasmodium falciparum PKG bound to 8-NBD-cGMP. The mixed intermediate state (dashed box) features an engaged pre-lid region to promote inhibitor binding, but the C-terminal lid remains disengaged to ensure inhibition [11]. The figure was reproduced with permission and was originally published in the Journal of Biological Chemistry. Byun JA, Van K, Huang J, Henning P, Franz E, Akimoto M, et al. Mechanism of allosteric inhibition in the Plasmodium falciparum cGMP-dependent protein kinase. J. Biol. Chem. 2020;295:8480–91. © the American Society for Biochemistry and Molecular Biology. (C) EPAC1 bound to I942. The mixed intermediate (dashed box) includes PBC “in” and C-terminal hinge helix (H) “out” conformations [13]. The out conformation of the hinge helix leads to inhibition of the catalytic region (CR), as it obstructs access to its Rap1 substrate. (D) EPAC1 bound to cAMP and CE3F4R, which uncompetitively binds to EPAC1 and stabilizes the mixed intermediate state (dashed box), where the PBC is “in” and the C-terminal hinge (H) is “out” [14]. The figures are adapted with permission from Boulton S, Selvaratnam R, Blondeau J-P, Lezoualc’h F, Melacini G. Mechanism of Selective Enzyme Inhibition through Uncompetitive Regulation of an Allosteric Agonist. J Am Chem Soc 2018;140:9624–37. Copyright 2018 American Chemical Society.