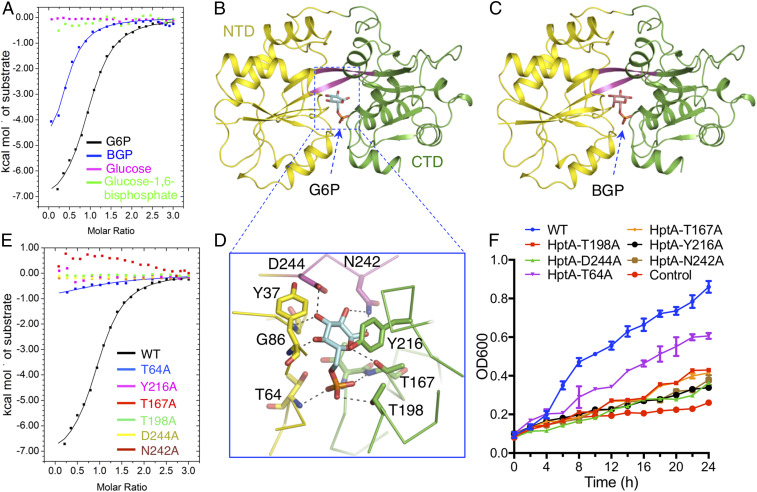
Fig. 1.
The ligand specificity of HptA. (A) ITC assays demonstrate that HptA interacts specifically with G6P and BGP. Structures of HptA in complex with G6P (B) and BGP (C). The HptA NTD, linker β-strand, and CTD are indicated by yellow, magenta, and green, respectively. G6P and BGP are shown in cyan and orange sticks, respectively. (D) The contacts between G6P and HptA residues in the ligand-binding site. (E) The G6P binding affinity of HptA mutants measured by ITC. (F) The growth kinetics in G6P-limited medium of ΔhptRSA S. aureus strains carrying HptRSA mutant constructs with the indicated single amino acid conversions in HptA. “Control” and “WT” represent the ΔhptRSA S. aureus strain transformed with the empty vector or plasmid containing a WT hptRSA gene cassette, respectively.