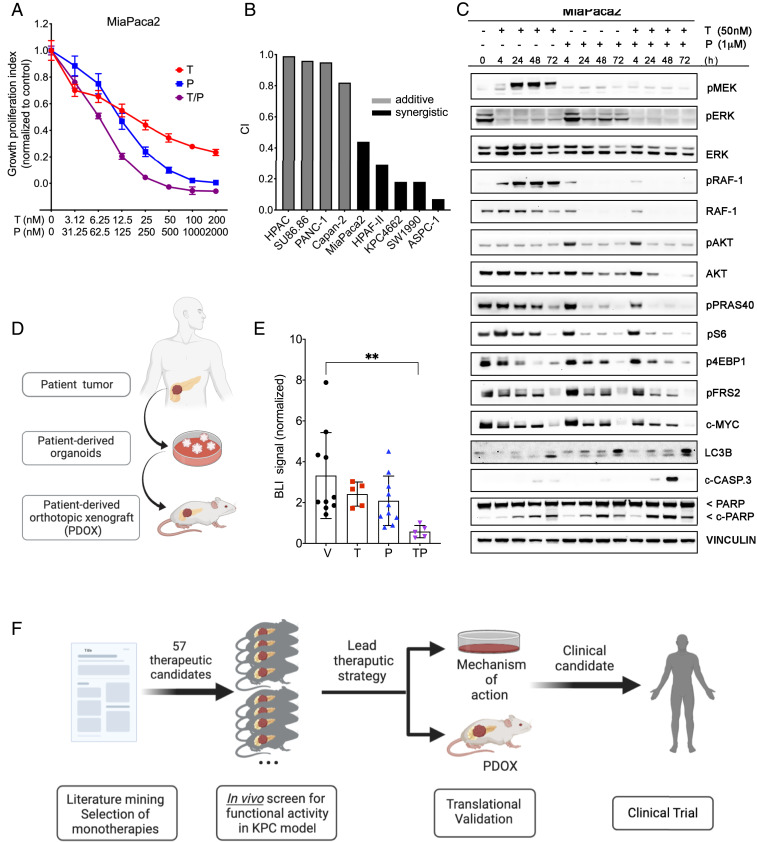
Fig. 4.
Trametinib and PU-H71 have antitumor activity in human PDAC models in vitro and in vivo. (A) Cell growth analysis of MiaPaca2 cells treated for 3 d with vehicle (DMSO) and increasing concentrations of trametinib (T), PU-H71 (P), or T/P. Cell viability was determined using the CTG assay and plotted as percentage of control. Representative results from three independent experiments are shown (n = 6, mean ± SEM, two-way ANOVA). (B) Drug synergism calculations for eight established human PDAC cell lines. Combination index (CI) < 0.75 indicates synergism, CI 0.75–1.25 indicates additive effects, and CI > 1.25 indicates antagonism. (C) Representative Western blotting of protein levels in MiaPaca2 cells following 4, 24, 48, and 72 h treatment with DMSO, trametinib (50 nM), and/or PU-H71 (1 μM). Note simultaneous and sustained inhibition of two major signaling pathways, MAPK and PI3K/AKT/mTOR, with the two-drug combination, unlike with either agent alone. Also note increase in cleaved PARP and cleaved caspase-3 levels in response to the T/P combination. (D) Schematic depicting generation of human patient-derived organoid (HPDO) lines. (E) Fold change in bioluminescence in NSG mice bearing orthotopic HPDO xenografts treated with vehicle, trametinib (2 mg/kg per day), PU-H71 (75 mg/kg per day) at day 14 normalized to the day before starting treatment (6 wk posttransplant) (mean ± SEM; n = 5 per group, **P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA). (F) Schematic outlining in vivo orthotopic transplant drug screening approach to identify novel candidate therapies.