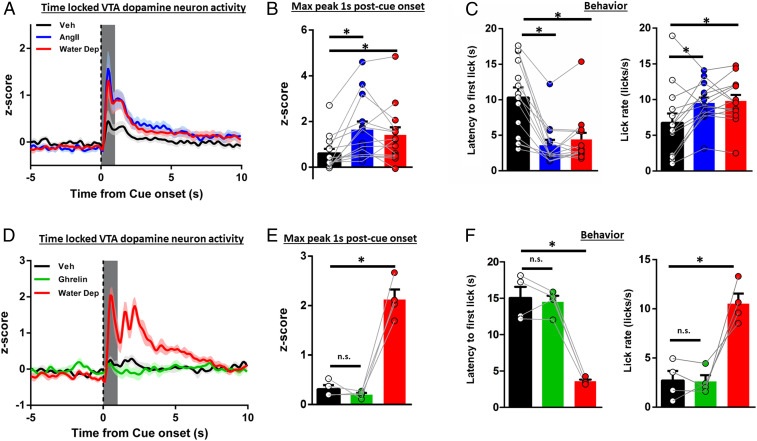
Fig. 3.
Central administration of AngII, but not ghrelin, potentiates water-cue-evoked phasic dopamine signaling in euvolemic rats. (A) VTA dopamine neuron activity time locked to cue onset (t = 0) in euvolemic vehicle, euvolemic AngII (10 ng/μL), or overnight water-deprived rats with quantification in B. (C) Latency to first lick and lick rate in euvolemic vehicle, euvolemic AngII, or water-deprived rats from A and B. (D) VTA dopamine neuron activity time locked to cue onset (t = 0) in euvolemic vehicle, euvolemic ghrelin (1 µg/μL) or overnight water-deprived rats with quantification in E. (F) Latency to first lick and lick rate in euvolemic vehicle, euvolemic ghrelin, or water-deprived rats from D–E. Dark lines in A and D are means and shading are SEM. Bars and whiskers in Insets are means SEM. Gray boxes in B and E represent 1-s time window postcue onset for quantification and analysis. *P < 0.05 vs. veh. n.s., not significant vs. veh.