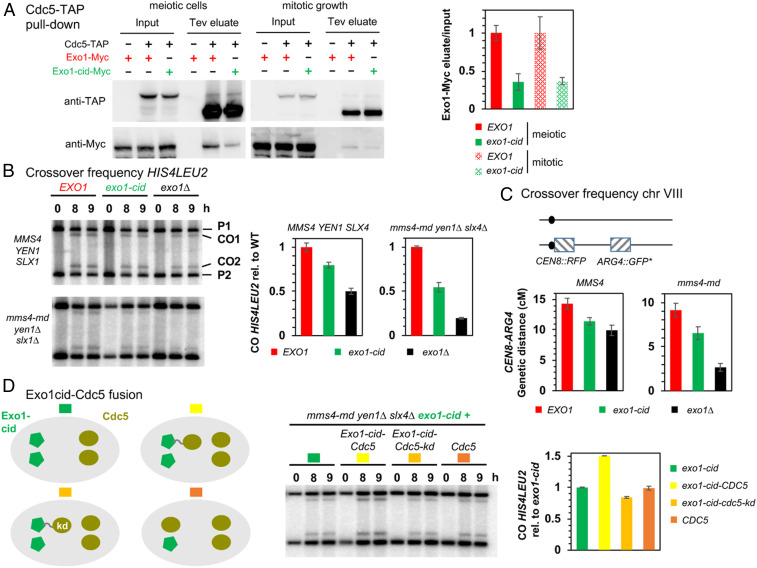
Fig. 6.
Cdc5 direct interaction with Exo1 promotes crossover formation. (A) Coimmunoprecipitation by Cdc5-TAP of Exo1-Myc in meiotic cells or in cells growing mitotically. Same conditions as in Fig. 4A. (Right) Quantification of Exo1-Myc levels in the Tev eluate relative to the input. Error bars represent SD of two independent experiments. (B) Meiotic crossover frequencies at the HIS4LEU2 hotspot in the exo1-cid mutant. (Left) Representative Southern blot analysis of crossovers in the indicated exo1 mutants, in an otherwise wild-type (MMS4 YEN1 SLX4) or triple nuclease mutant (mms4-md yen1∆ slx4∆) background. mms4-md stands for pCLB2-mms4. (Right) Quantification of crossovers. Values are the mean ± SEM of four independent experiments (wild-type background) or mean ± SD of two independent experiments (triple nuclease mutant), normalized to the corresponding EXO1 value. (C) Meiotic crossovers on chromosome VIII. (Left) Illustration of the fluorescent spore set-up (78). (Right) Genetic distances measured in the CEN8-ARG4 genetic interval for each indicated genotype. (D) Meiotic crossover frequencies at the HIS4LEU2 hotspot with an Exo1-cid–Cdc5 fusion protein. (Left) Scheme illustrating the different experimental setups. In each cell, proteins are expressed from the two allelic endogenous EXO1 promoters (Left) or CDC5 promoters (Right). Same legend as in B. Values are the mean ± SD of two independent experiments, normalized to the homozygous exo1-cid-Myc value.