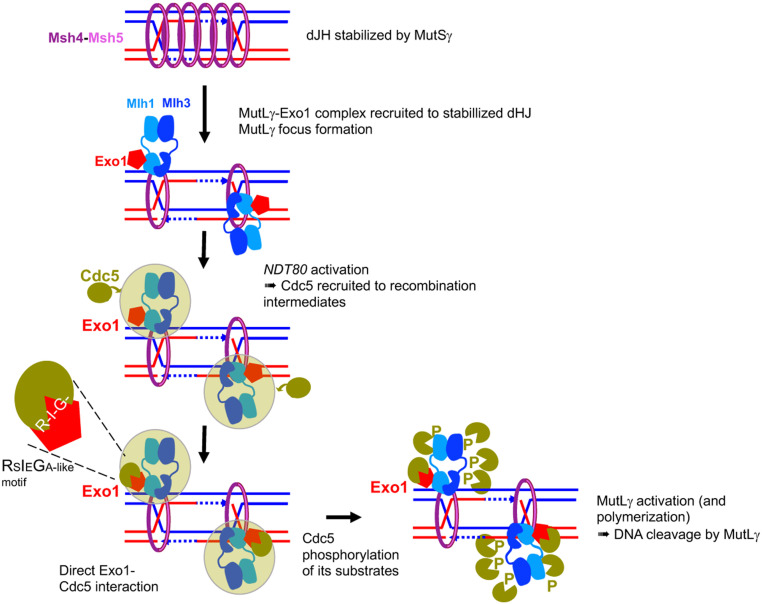
Fig. 7.
Model of MutLγ binding to sites of recombination and activation for crossover formation. MutSγ stabilizes dHJ intermediates and forms foci on chromosomes. MutLγ, in complex with Exo1, binds dJH intermediates that have been stabilized by MutSγ and other ZMM proteins. For simplicity, MutSγ is shown embracing both DNA duplexes of the intermediates, but recent data also suggest it may embrace separately each DNA duplex (74). Once bound on the dHJ, MutLγ may form a focus when interacting with MutSγ (model shown here), or later in the process of its activation (not shown). Upon NDT80 activation, the Cdc5 kinase is induced, and interacts with the MutLγ–Exo1 complex through multiple interactions (green cloud). Among these interactions, the direct interaction of Cdc5 with Exo1 is important for MutLγ-driven crossover formation. We propose that this interaction allows Cdc5 to phosphorylate MutLγ, which activates its nuclease function and produces crossover formation. This may occur through transient MutLγ polymerization.