Fig. 1.
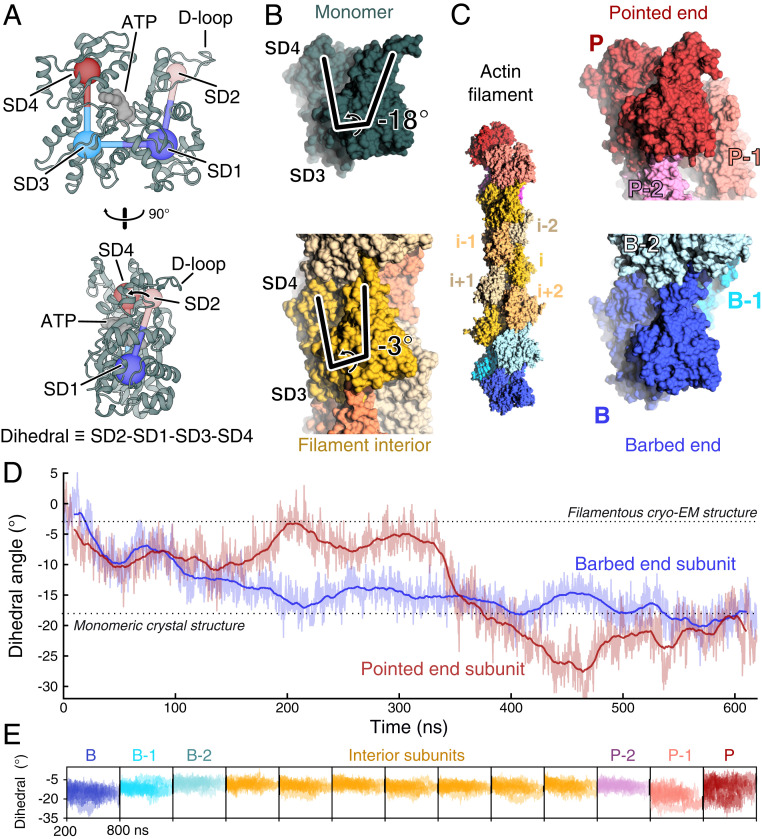
The terminal subunits of actin filaments take on monomer-like conformations. (A) Two orientations of a ribbon diagram of the ATP-bound actin monomer with labels on the four subdomains, SD1 through 4. The dihedral angle defined by SD2-SD1-SD3-SD4 characterizes the primary structural transition between monomeric actin and polymerized, filamentous actin. The flexible D-loop in SD2 forms stabilizing contacts between subunits. PDB entry 3TU5. (B) Side views of space-filling models of monomeric actin (dark green, PDB 3TU5) and a subunit within a filament (yellow, PDB 6JDM). The lines highlight the difference in the dihedral angle between actin monomers (−18°) and a subunit in a filament (−3°). The models are aligned by subdomains 3 and 4. (C, Left) Space-filling model from the second half of a 620-ns molecular dynamics simulation of an ATP-actin 13-mer. Note that the terminal subunits at the barbed end (B, blue) and pointed end (P, red) lack two neighboring subunits that form contacts between interior subunits. The penultimate subunits B-1 and P-1 each lack one neighboring subunit. (C, Right) Zoom in on the filament ends showing the terminal subunits B and P in conformations closely resembling monomers. Subunits B and P are aligned relative to each other by subdomains 3 and 4. (D) Time course of changes of the dihedral angle of the terminal P and B subunits during a 620-ns simulation of the ATP-actin filament, in which all subunits started in the conformation of interior subunits (PDB 6DJM). During the simulation, both terminal subunits transitioned spontaneously from the filamentous conformation toward the monomer conformation. Raw data (light) and 20-ns moving average (dark) are shown. Data and snapshots are from simulation 3 (SI Appendix, Table S1). (E) Time courses of the dihedral angles of each subunit in the 13-mer actin filaments for times greater than 200 ns. Nine runs are shown (simulations 1 to 9) (SI Appendix, Table S1). Subunits at the filament ends sample a wider range of conformations than the flattened internal subunits (yellow).