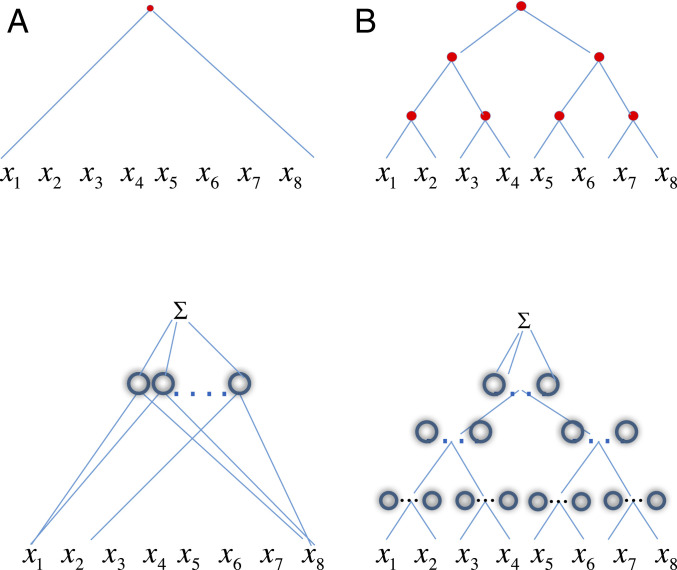
Fig. 1.
Top graphs are associated to functions. Each Bottom diagram (Insets) depicts the ideal network approximating the function above. (Inset A) A shallow universal network in 8 variables and units approximates a generic function of 8 variables . (Inset B) A hierarchical network at the bottom in variables, which approximates well functions of the form as represented by the binary graph above. In the approximating network each of the nodes in the graph of the function corresponds to a set of ReLU units. Similar to the shallow network, a hierarchical network is universal; that is, it can approximate any continuous function; the text discusses how it can approximate a subclass of compositional functions exponentially better than a shallow network. Redrawn from ref. 23.