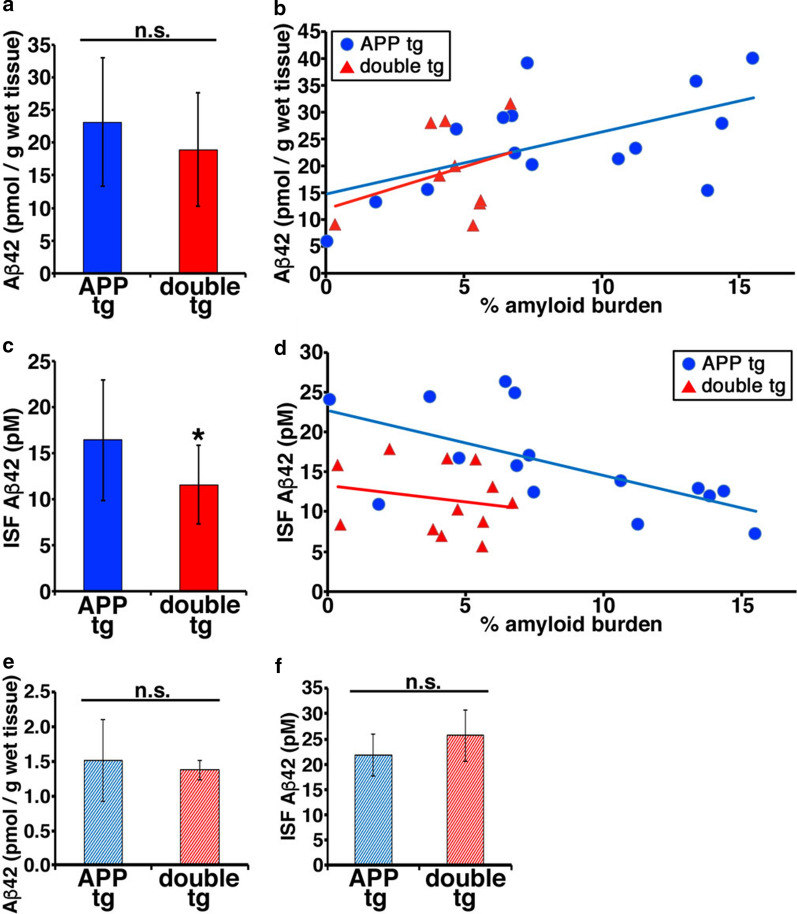
Fig. 8.
ISF Aβ in the brain of double tg was significantly decreased compared with APP tg. a The concentration of Aβ42 (pmol/g wet tissue) in the TBS-soluble fraction of the brains of 18–19-month-old APP tg (A7 line) and double tg mice. N = 13 (APP tg), and 9 (double tg). The mean ± SD Student’s t-test, p = 0.31 n.s. means no significant difference. b Correlation between the concentration of TBS-soluble Aβ42 and area of Aβ deposits in hippocamps of the brains of 18–22-month-old APP and double tg mice. R2 = 0.322 (APP tg), R2 = 0.108 (double tg). c The concentration of Aβ42 (pM) in brain ISF of 18–19-month-old APP and double tg mice. N = 13 (APP tg), and 12 (double tg). The mean ± SD Student’s t-test, p = 0.040. d Correlation between the concentration of ISF Aβ42 and area of Aβ deposits in hippocamps of the brains of 18–22-month-old APP and double tg mice. R2 = 0.385 (APP tg), R2 = 0.0416 (double tg). e The concentration of Aβ42 (pmol/g wet tissue) in the TBS-soluble fraction of the brains of 5–7-month-old APP and double tg mice. N = 4 (APP tg), and 4 (double tg). The mean ± SD Welch’s t-test, p = 0.67. n.s. means no significant difference. f The concentration of ISF Aβ42 (pM) in the brains of 5–7-month-old APP and double tg mice. N = 4 (APP tg), and 4 (double tg). The mean ± SD Student’s t-test, p = 0.28. n.s. means no significant difference