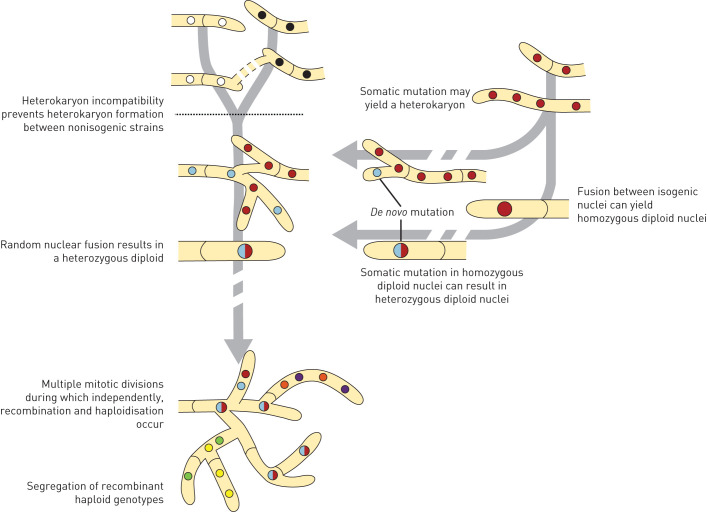
FIGURE 5.
The parasexual cycle in Aspergillus fumigatus. Parasexual recombination can be achieved for most fungi in laboratory experiments and is characterised by heterokaryon formation, heterozygous diploid formation, recombination and haploidisation. Heterokaryon incompatibility normally prevents parasexual recombination between non-isogenic strains in A. fumigatus (dashed black line), but in this study we show that during long-lasting fungal colonisation of the human lung, sufficient isogenic genetic variation is generated to make parasexual recombination of A. fumigatus effective. Somatic mutation may yield a heterokaryon or fusion of isogenic nuclei may yield a homozygous diploid which can both subsequently evolve into a heterozygous diploid by de novo mutations. A heterozygous diploid can continue to accumulate mutations or finally after haploidisation segregate into new recombinant genotypes.