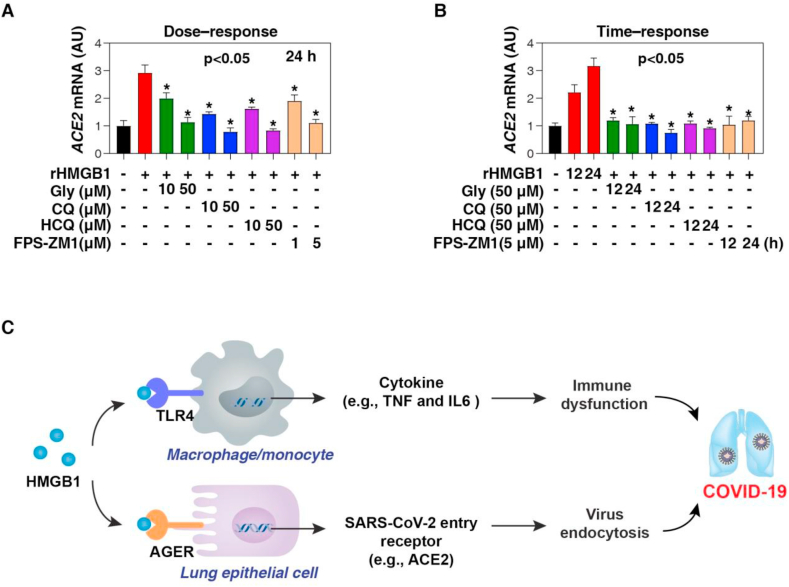
Figure 4.
Pharmacological inhibition of HMGB1-AGER signaling limits ACE2 expression. (A, B) Q-PCR analysis of ACE2 mRNA in indicated Calu-3 cells following treatment with human HMGB1 protein (200 ng/ml) in the absence or presence of glycyrrhizin (Gly), chloroquine (CQ), hydroxychloroquine (HCQ), and AGER inhibitor FPS-ZM1 for 12 or 24 h (n = 3, ∗P < 0.05 versus HMGB1 group, ANOVA test). (C) Schematic depiction of the role of HMGB1 release in COVID-19. HMGB1 may be involved in COVID-19 through at least two mechanisms: one is TLR4-mediated cytokine storm in immune cells (e.g., macrophages and monocytes), and the other is AGER-mediated ACE2 expression in alveolar epithelial cells. Data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments, each performed in triplicate, and are presented relative to control.