Figure 1.
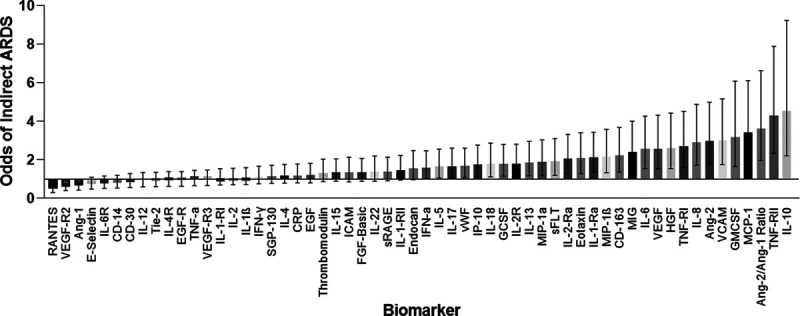
Odds of indirect acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS) by biomarker. Logistic regression was used to determine the association between biomarker and ARDS subtype. Odds ratio (OR) < 1 indicates an association with direct ARDS and OR > 1 indicates an association with indirect ARDS. Whiskers represent 95% CI. Ang = angiopoietin, ARDS = acute respiratory distress syndrome, CD = cluster of differentiation, CRP = C-reactive protein, EGF = epidermal growth factor, FGF = fibroblast growth factor, GCSF = granulocyte colony-stimulating factor, GMCSF = granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor, HGF = hepatocyte growth factor, ICAM = intracellular adhesion molecule, IFN = interferon, IL = interleukin, IP = interferon gamma-induced protein, MCP = monocyte chemoattractant protein, MIG = monocyte induced by interferon γ, MIP = macrophage inflammatory protein, –R = –receptor, RANTES = regulated on activation, normal T cell expressed and secreted, sFLT = soluble fms-like tyrosine kinase, SGP = serum glycoprotein, sRAGE = soluble receptor for advanced glycation end-products, Tie-2 = tyrosine kinase with immunoglobulin-like loop epidermal growth factor homology domain 2, TNF = tumor necrosis factor, VCAM = vascular adhesion molecule, VEGF = vascular endothelial growth factor, vWF = von Willebrand factor.
