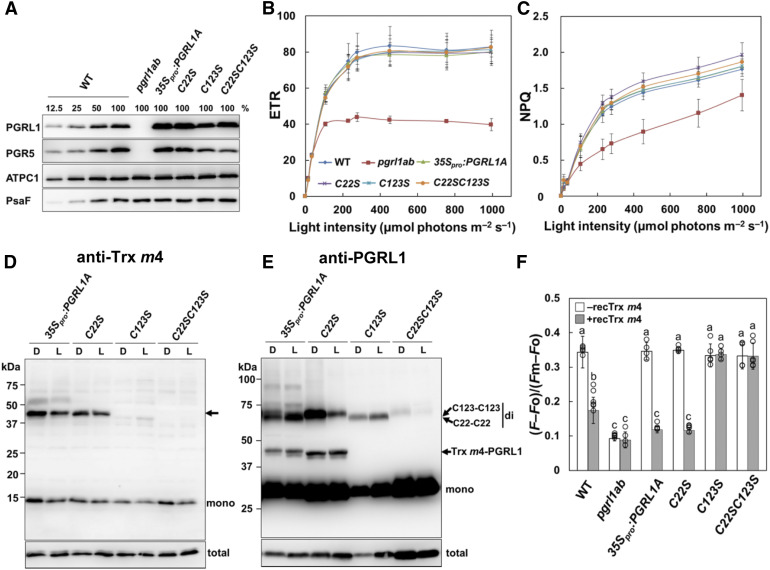
Figure 7.
Characterization of PGRL1 Cys Variants.
(A) Immunoblot analysis of PGRL1 in the 35Spro:PGRL1A Cys variant lines. PGRL1, PGR5, ATPC1, and PsaF were immunodetected using specific antibodies. Lanes were loaded with thylakoid membranes corresponding to 1.0 µg of chlorophyll (100%) from the wild type (WT), pgrl1ab, and the 35Spro:PGRL1A, C22S, C123, and C22SC123S Cys variant lines, along with a dilution series of WT sample.
(B) In vivo analysis of electron transport activity. Light intensity dependence of ETR. Each data point represents the mean ± sd (n = 5 independent plants). WT, wild type.
(C) Light intensity dependence of NPQ of chlorophyll fluorescence. Each data point represents the mean ± sd (n = 5 independent plants).
(D) and (E) Detection of the Trx m4-PGRL1 complex on nonreducing SDS-PAGE. Protein samples were extracted from dark-adapted (D) or growth light–incubated (L; 50 µmol photons m–2 s–1) leaves and immunodetected using Trx m4 (D) and PGRL1 (E) antibodies. Arrow in (D) indicates the Trx m4-PGRL1 complex. “mono” and “di” indicate monomer and dimer, respectively. C22-C22 and C123-C123 indicate dimers formed via intermolecular disulfide bonds between Cys-22 and Cys-22 or Cys-123 and Cys-123 of two PGRL1 monomers, respectively. The total amount of Trx m4 or PGRL1 protein (Total) was analyzed on reducing SDS-PAGE to cleave disulfide bonds of complexes, in the same volume used in the detection of the Trx m4-PGRL1 complex. To detect the Trx m4-PGRL1 complex, the chemiluminescence signal of PGRL1 monomer was oversaturated.
(F) Effect of the reduced Trx m4 on the Fd-dependent PQ reduction. Activity of Fd-dependent PQ reduction (Supplemental Figures 6B to 6D) was evaluated using the equation (F – Fo)/(Fm – Fo). White bars indicate chloroplast preparations without Trx m4; gray bars indicate chloroplast preparations with 5 µM of reduced Trx m4. Each value represents the mean ± sd of four to six independent ruptured chloroplast preparations. Columns with the same letters are not significantly different between genotypes (Tukey–Kramer test, P < 0.05). WT, wild type.