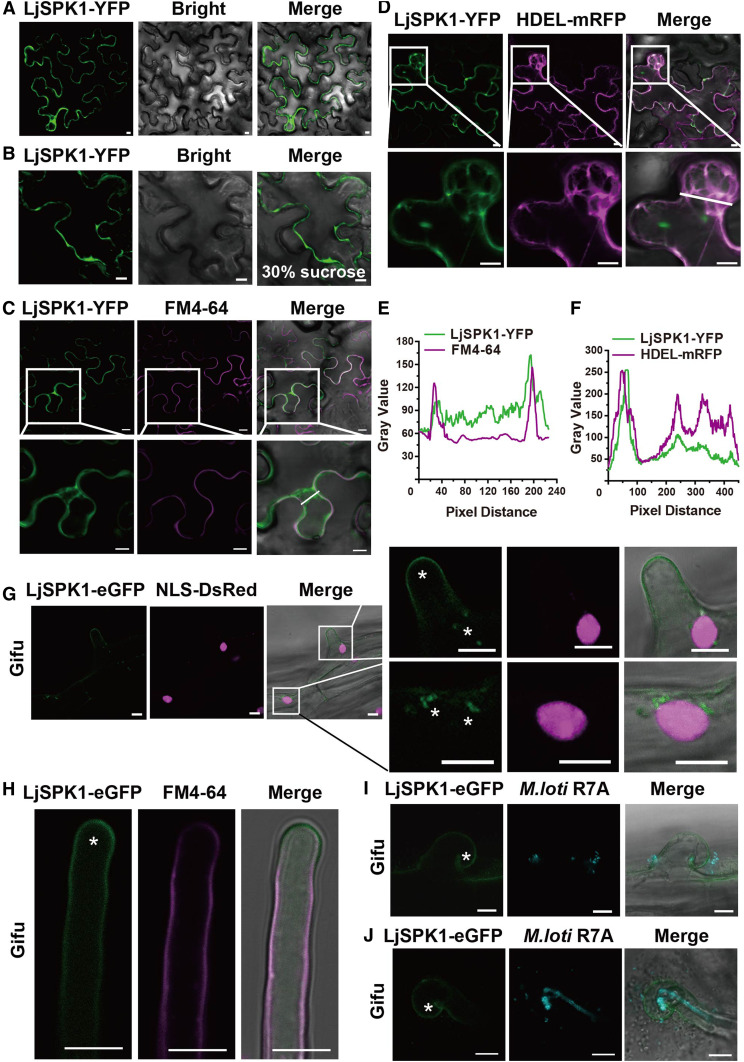
Figure 6.
Subcellular Localization of LjSPK1 in N. benthamiana Leaves and Wild-Type L. japonicus Hairy Roots.
(A) to (F) Confocal images of LjSPK1-YFP expressed in N. benthamiana leaf cells. (A) and (B) Subcellular localization of LjSPK1-YFP in N. benthamiana leaves (A) and after plasmolysis via 30% (w/v) Suc treatment (B). (C) LjSPK1-YFP (green) expressed in N. benthamiana leaves and stained with the PM marker FM4-64 dye (magenta), showing that SPK1 does not merge with the PM marker. (D) LjSPK1-YFP (green) and ER marker HDEL-mRFP (magenta) were coexpressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Image shows merging of LjSPK1-YFP and HDEL-mRFP fluorescence. These genes were driven by the CaMV 35S promoter. (E) and (F) Intensity profiles of LjSPK1 and FM4-64 or HDEL-mRFP. Plots show fluorescence intensities of LjSPK1-YFP (green) and FM4-64 or HDEL-mRFP (magenta) in regions of interest (insets in [C] and [D]). (C) and (D) Insets (bottom) are enlargements of the areas in white boxes (top). Bars = 10 μm.
(G) to (J) Live cell confocal images of LjSPK1-eGFP expressed in root hairs before (G) and (H) and after (I) and (J) M. loti R7A/mTag inoculation in wild-type L. japonicus hairy roots. (G) LjSPK1-eGFP (green) fluorescence was detected in L. japonicus hairy roots in the PM and puncta in the vicinity of the nucleus. NLS-DsRed (magenta; nuclear marker) was used as a transgenic marker. (H) LjSPK1-eGFP (green) was detected in L. japonicus hairy root PM and stained with the PM marker FM4-64 dye (magenta). (I) and (J) LjSPK1-eGFP (green) in the PM of curled root hair (I) or with elongated IT (J) after M. loti R7A/mTag inoculation. IT is indicated by M. loti R7A/mTag (cyan). Asterisks indicate GFP fluorescence. Expression of LjSPK1 was driven by the L. japonicus Ubiquitin gene promoter. Insets (right) are enlargements of the areas in white boxes (left). Bars = 10 μm.