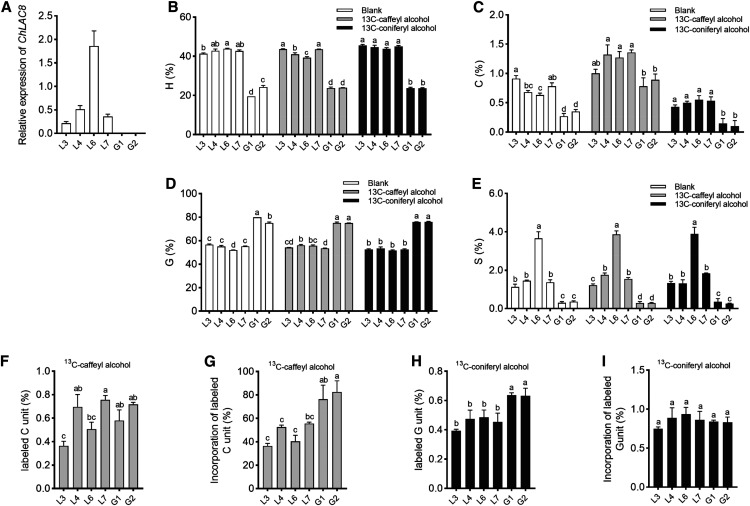
Figure 7.
Incorporation of Exogenous Monolignols into Lignin of M. truncatula comt Mutant Hairy Root Cultures Expressing ChLAC8.
(A) ChLAC8 transcript levels as determined by qRT-PCR, expressed relative to Tubulin as a housekeeping gene.
(B) to (E) Lignin monomer thioacidolysis yields for hydroxyphenyl (A), caffeyl (B), guaiacyl (C),and syringyl (D) lignin units in the hairy roots. The yields for 5HG were under the limit of quantification. Values shown are percentages of total lignin units in hairy root tissues.
(F) and (H) Lignin monomer thioacidolysis yields for labeled caffeyl (F) and guaiacyl (H) units in the hairy roots when 13C6-caffeyl (F) or 13C6-coniferyl (G) alcohols were applied, respectively. No labeled guaiacyl (F) or syringyl (H) units were detected. Values shown are percentages of total lignin units in hairy root tissues.
(G) and (I) Percentage incorporation of 13C6-caffeyl (G) or 13C6-coniferyl (I) alcohols into caffeyl (G) and guaiacyl (I) units of lignin.
Hairy root sections were incubated with 100 μM of 13C6-caffeyl alcohol or 13C6-coniferyl alcohol for 2 d before extraction of lignin and analysis by thioacidolysis. Four independent lines expressing ChLAC8 (L) were analyzed and compared with two lines expressing GUS (G), all in the comt mutant background. For each biological replicate, ∼100 mg of hairy root cultures harvested from one tissue culture dish was put into one well. Data are means of three biological replicates (after averaging two analytical replicates). Error bars indicate ses. The different letters above the bars represent statistically significant differences determined by one-way ANOVA (Duncan, P ≤ 0.05) with the software SPSS Statistics (v.22; IBM).