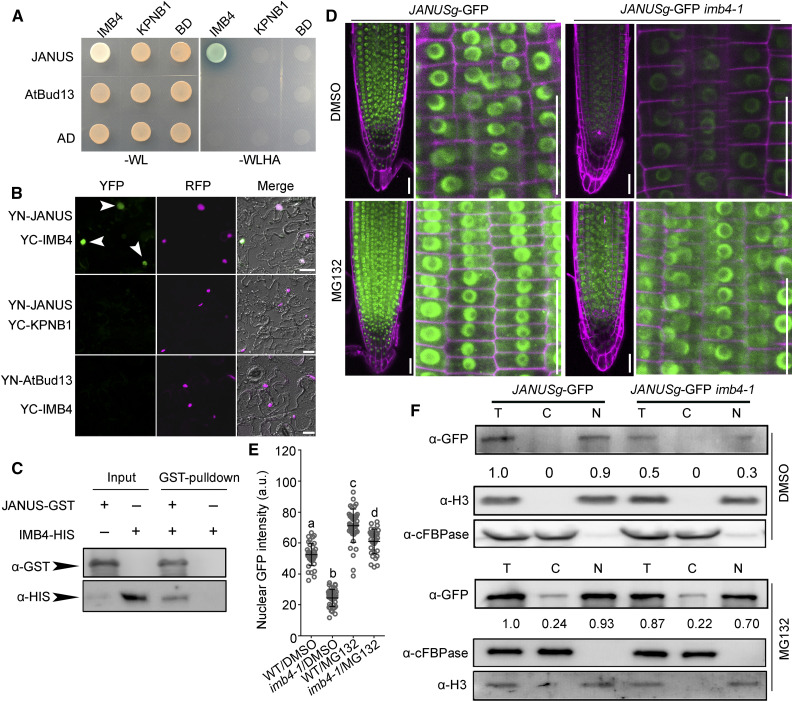
Figure 2.
IMB4 Mediates the Nuclear Accumulation of JANUS.
(A) and (B) Y2H (A) and BiFC (B) assays demonstrating the specific interaction between JANUS and IMB4. KPNB1, another Arabidopsis importin β (Luo et al., 2013), was used as a negative control for IMB4, while AtBud13, another component of the spliceosome (Xiong et al., 2019b), was used as a negative control for JANUS. Yeast colonies bearing both the BD and AD vectors were selected on synthetic minimal medium lacking Trp and Leu (–WL); positive interaction was assessed on synthetic minimal medium lacking Trp, Leu, His, and Ade (–WLHA). Bars in (B) = 50 μm.
(C) In vitro pull-down assay. Results are representative of three biological replicates.
(D) and (E) Representative CLSM images (D) and GFP intensities (E) of RAM from JANUSg-GFP in the wild type and JANUSg-GFP in imb4-1 upon DMSO or MG132 treatment. a.u. indicates arbitrary units. Roots were stained with PI (magenta). Images were taken from seedling roots at 5 DAG treated with DMSO or 100 μM MG132 for 2 h. Values are means ± se (n = 20). Fluorescence of the nuclei in the root meristem zone was measured. Different letters indicate significantly different groups (one-way ANOVA, Tukey’s multiple comparisons test, P < 0.05). Bars in (D) = 50 μm.
(F) Cell fractionation and immunoblot analysis. Anti-GFP antibody was used in immunoblots to detect JANUS-GFP. Numbers at the bottom are the values of JANUS-GFP in the nuclear fraction (N) or cytoplasmic fraction (C) relative to that of the total protein fraction (T), which was set to 1. Anti-histone H3 and anti-cFBPase were used to indicate nuclear and cytoplasmic fractions, respectively.