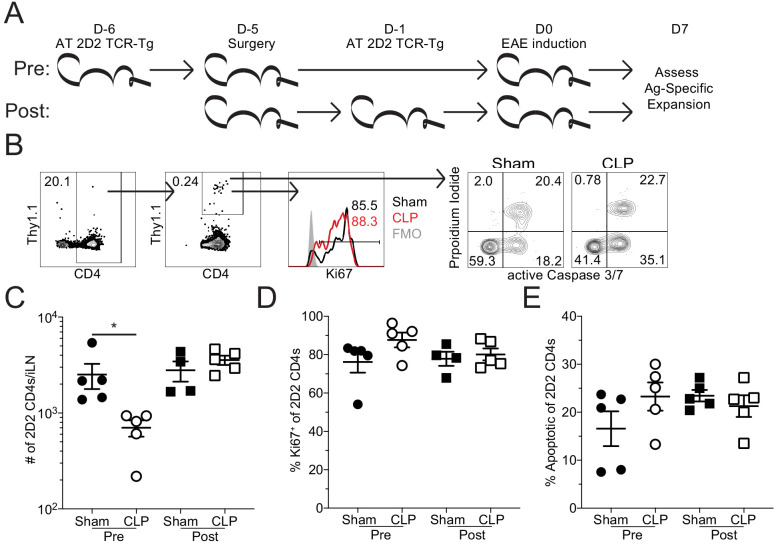
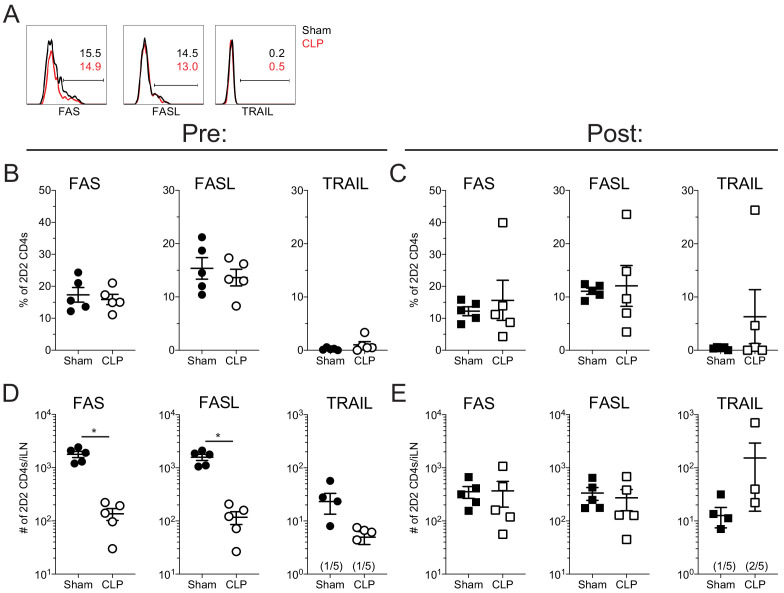
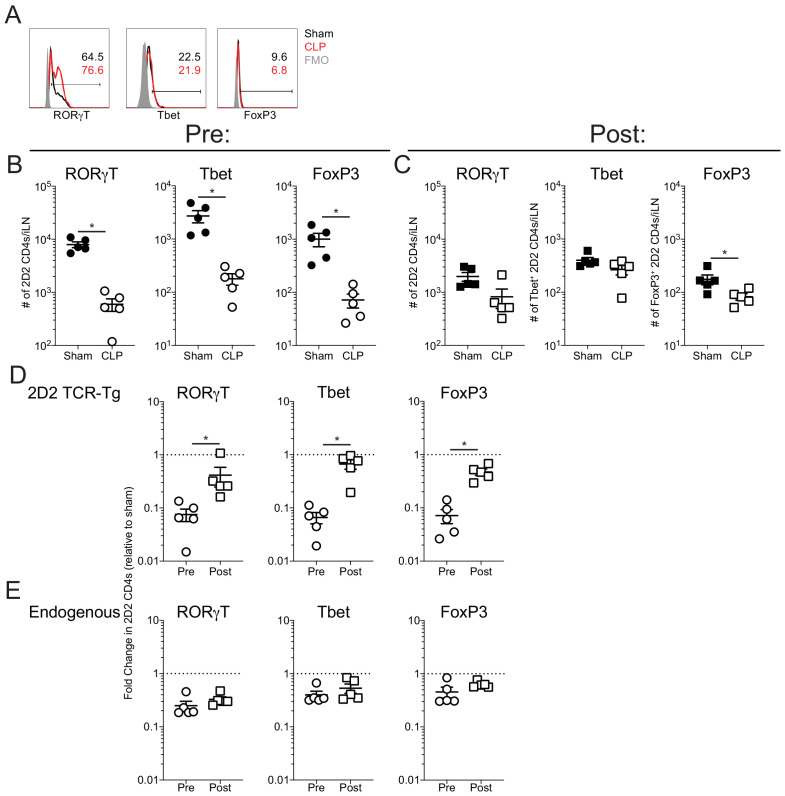
Figure 6. Sepsis reduces the number of MOG-specific CD4 T cells but not their capacity to proliferate.
(A) Experimental design: Thy1.2 C57Bl/6 mice were separated into Pre- and Post-transfer groups. The Pre-transfer group received 5 × 103 naive Thy1.1 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells 1 day before sham or CLP surgery. The Post-transfer group underwent sham or CLP surgery then received 5 × 103 naive Thy1.1 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells 4 days later. EAE was induced in both the Pre- and Post-transfer groups 5 days after surgery (Pre: 6 days post 2D2 T cell transfer; Post: 1 day post 2D2 T cell transfer). iLN were harvested 7 days after the transfer. (B) Representative gating strategy for identifying transferred 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells, their expression of the proliferation marker Ki67, and markers of apoptosis (activated caspase3/7 with propidium iodide) from sham and CLP mice. (C) Number of transferred 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells in the iLN of sham and CLP mice. (D) Frequency of 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells expressing Ki67. (D) Frequency of apoptotic (FLICA+ PI+) 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells. Data are representative from two independent experiments with four to five mice per group. *p<0.05. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.