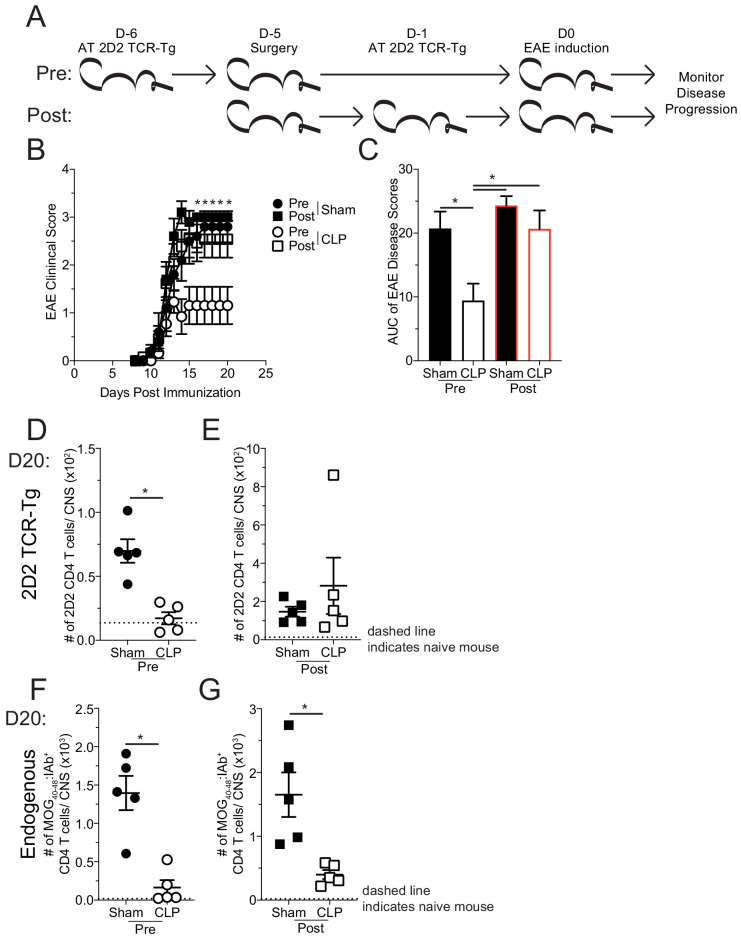
Figure 8. Sepsis-induced numerical loss of MOG-specific naive CD4 T cell precursors diminishes EAE disease development.
(A) Experimental design: Thy1.2 C57Bl/6 mice were separated into Pre- and Post-transfer groups. The Pre-transfer group received 5 × 103 naive Thy1.1 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells 1 day before sham or CLP surgery. The Post-transfer group underwent sham or CLP surgery then received 5 × 103 naive Thy1.1 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells 4 days later. EAE was induced in both the Pre- and Post-transfer groups 5 days after surgery (Pre: 6 days post 2D2 T cell transfer; Post: 1 day post 2D2 T cell transfer). EAE disease onset and severity were monitored. (B) Average EAE disease score following EAE induction for mice that were Pre-transfer sham (black circle), Post-transfer sham (black square), Pre-transfer CLP (white circle), or Post-transfer CLP (white square). (C) Area under the curve (AUC) of disease scores in panel B following EAE induction. Number of 2D2 TCR-Tg CD4 T cells in the CNS of sham and CLP (D) Pre-transfer and (E) Post-transfer groups as well as endogenous MOG-specific CD4 T cells in the CNS of sham and CLP for (F) Pre-transfer and (G) Post-transfer groups. Data are representative from two independent experiments with 10–14 mice per group for panels B and C, and five mice per group for panels D-G. *p<0.05. Error bars represent the standard error of the mean.