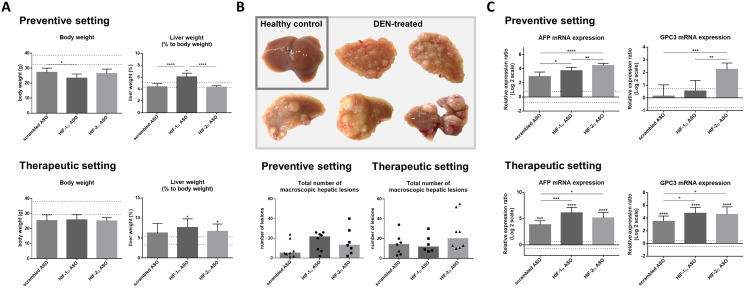
Figure 4. Effect of preventive and therapeutic HIF-1α and HIF-2α ASO treatment on hepatocarcinogenesis in DEN-induced HCC mice.
HCC was induced by weekly intraperitoneal DEN injection for 25 weeks. Control mice received weekly intraperitoneal 0.9% NaCl injection. DEN-treated mice were intraperitoneally injected with 20 mg/kg HIF-1α ASO, HIF-2α ASO or scrambled ASO twice per week, in either a preventive or a therapeutic setting. Control mice received scrambled ASO for the same duration of the experiment. (A) Body weight and relative liver weight (expressed as % to body weight) following preventive and therapeutic treatment. The upper and lower dashed lines represent mean ± SD of the control mice. Bars represent mean ± SD of different treatment groups of DEN-treated mice (n = 6–8 per treatment group). (B) Upper part: Hepatic tissue of healthy control mice and DEN-treated mice. Lower part: Total number of macroscopic hepatic lesions following preventive and therapeutic treatment. Data are represented as individual values with the median (n = 6–8 per treatment group). (C) Hepatic mRNA expression of the HCC tumor markers AFP and GPC3 following preventive and therapeutic treatment. The upper and lower dashed lines represent log2-transformed mean ± SD of the control mice. Bars represent log2-transformed mean ± SD of different treatment groups of DEN-treated mice, relative to the log2-transformed mean of the control mice (n = 7–9 per treatment group). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.