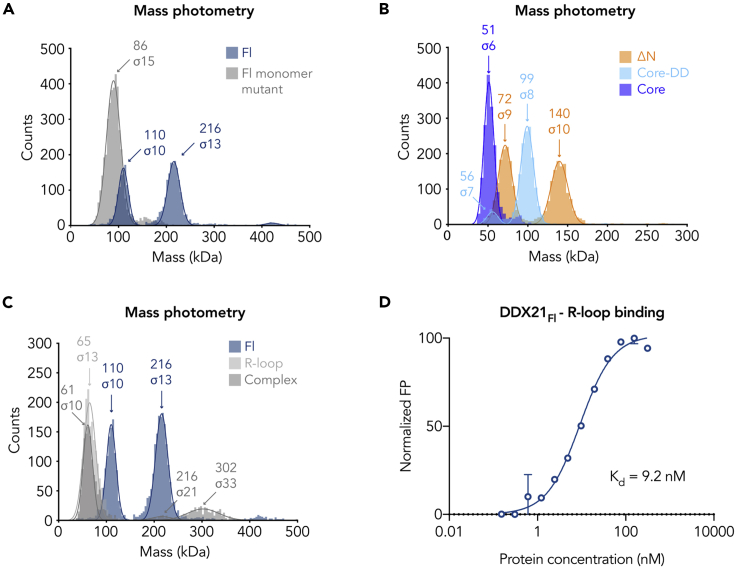
Figure 2.
The DDX21 Dimer Binds Two R-loop Molecules
(A) Mass photometric profiles obtained for DDX21Fl (in blue) and DDX21Fl monomer mutant (in gray) with the determined average molecular mass indicated above each peak. The theoretical molar mass for DDX21Fl (with uncleaved affinity tag) is 104.9 kDa and for the DDX21Fl monomer mutant is 90 kDa. The wild-type protein shows a monomer-dimer equilibrium, whereas the mutant is mainly monomeric.
(B) Mass photometric profiles for DDX21ΔN, DDX21Core-DD, and DDX21core indicate that DDX21ΔN displays a monomer-dimer equilibrium as seen for DDX21Fl, whereas DDX21Core-DD and DDX21core are mainly dimeric and monomeric, respectively.
(C) Mass photometric profile for the DDX21Fl-R-loop complex at 30 nM. (D) Fluorescence polarization binding assays measure a binding affinity of DDX21Fl to the R-loop substrate of 9.2 ± 0.7 nM. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent measurements. The mass photometric experiments were performed in duplicates for the protein samples and in triplicates for the R-loop complex (see also Figure S6).