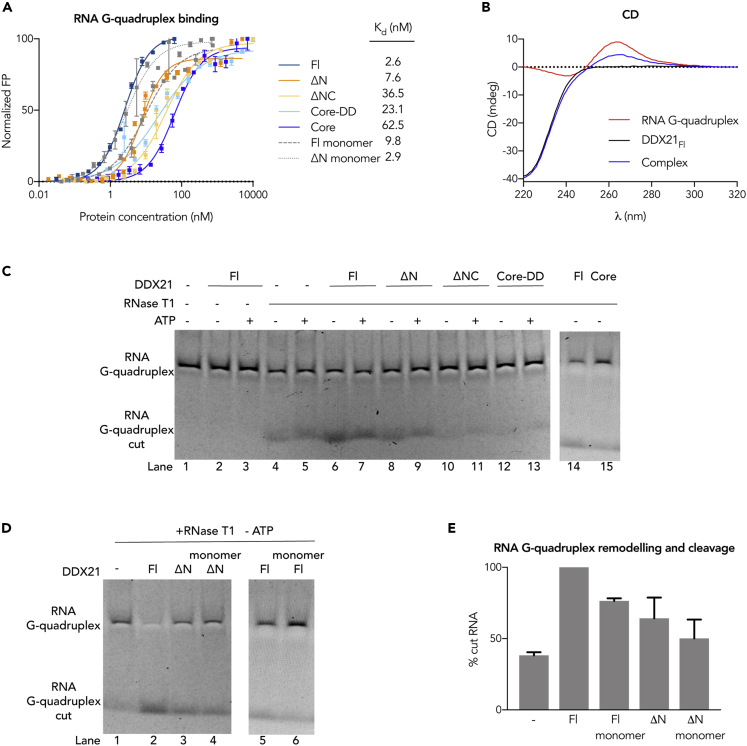
Figure 4.
DDX21 Activity on RNA G-Quadruplexes
(A) FP binding curves for the different DDX21 variants and the RNA G-quadruplex Q2. Error bars represent the standard deviation of three independent measurements (see also Figure S9 and Table S2).
(B) The circular dichroism (CD) spectra of the RNA G-quadruplex (in red) with a parallel structure with its characteristic maximum at 260 nm and minimum at 240 nm. In the presence of DDX21Fl (blue), this structure is maintained, as showed by the maximum at 260 nm that is not present in the spectrum of the protein alone (black) (see also Figure S10).
(C and D) RNA G-quadruplex remodeling assay comparing the activity of the different DDX21 mutants. In native condition polyacrylamide gels, the 5′-FAM-labeled RNA was visualized by measuring the fluorescent signal at 535 nm. The activity was calculated by measuring the intensity of the product (cut) RNA bands, with respect to DDX21Fl activity.
(E) Quantification of the G-quadruplex remodeling assay for the constructs with activity above background: Fl, ΔN, and the monomeric ΔN and Fl mutants. The graph on the right summarizes the results from three independent experiments (see also Figure S11). Error bars represent the standard deviation.