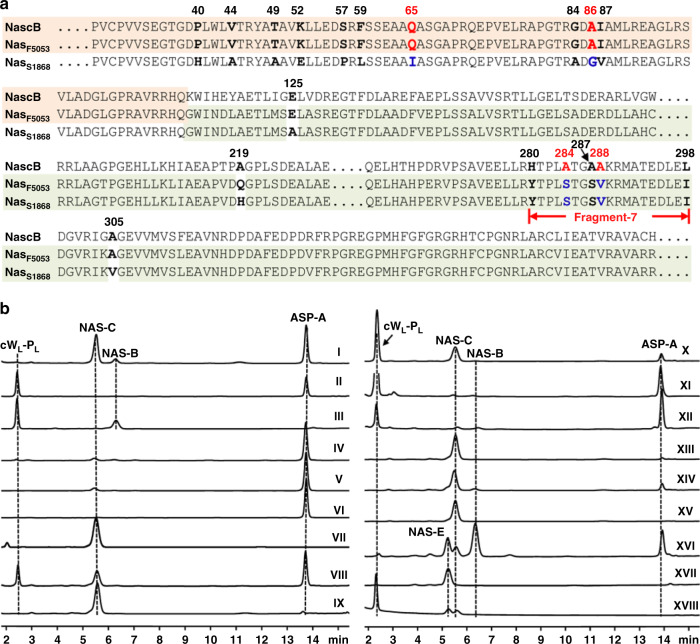
Fig. 2. Deciphering and engineering the regio-specificity and stereo-specificity of HTDKP forming P450s.
a The sequence alignments of NascB, NascF5053, and NasS1868. The identical N-terminal and C-terminal parts of NascB/NasF5053 and NasF5053/NasS1868 are shaded in orange and light green, respectively. Residues less important are not shown and indicated by dashed lines. The four critical residues are bolded and highlighted by colors. b In vitro characterization of P450s and their mutants using cWL-PL as substrate. (I) NascF5053; (II) NasS1868; (III) NasbB; (IV) NasF5053-Q65I; (V) NasF5053-A86G; (VI) NasF5053-Q65I-A86G; (VII) NascB; (VIII) NascB-Q65I; (IX) NascB-A86G; (X) NascB-Q65I-A86G; (XI) NascB-S1868fragment-7; (XII) NascB-Q65I-A86G-A284S-A288V; (XIII) NascF5053-S284A; (XIV) NascF5053-V288A; (XV) NascF5053-S284A-V288A; (XVI) NascF5053-A86K-V288P; (XVII) NAS-E synthetic standard; (XVIII) NascF5053-Q65P-A86W-S284C.