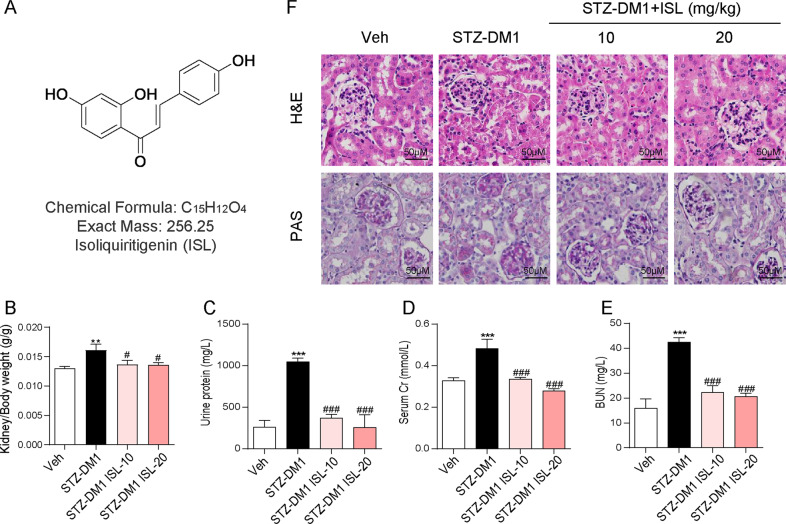
Fig. 1. ISL attenuated hyperglycemia-induced renal histological abnormalities and biochemical indicators increase.
Diabetes mellitus was induced by streptozotocin (STZ), which dissolved in 0.1 mol/L sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5) for intraperitoneal injection at 50 mg/kg/day that lasted 5 days. The mice with fasting-blood glucose levels exceeding 12 mM were considered diabetic. Diabetic mice were then subject to oral treatment using ISL (10 or 20 mg/kg) or vehicle (0.5% CMC-Na) by gavage every other day for 12 weeks (n = 7 in each group). 24 h before the conclusion of experiment, mice urine was collected. After killing, kidney tissues of the mice were collected and blood samples centrifuged to collect serum for further analysis. a The structure of ISL. b The kidney/body weight ratio. c Total protein concentration in urine. d The level of serum creatinine. e The level of serum BUN. f Representative images for H&E staining and PAS staining using the formalin-fixed renal tissues as described in Methods and materials (×400 magnification) (A minimum of five mice in each group were used for analysis. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 vs control (Veh); #P < 0.05, ###P < 0.001 vs STZ1-DM).