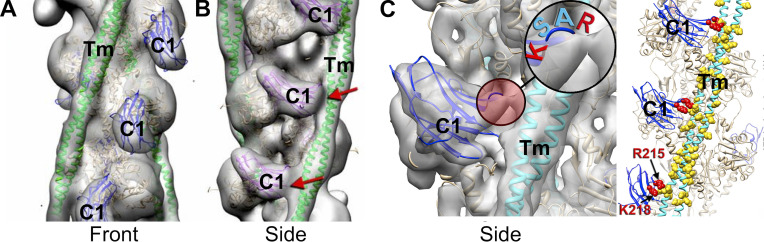
Figure 3.
Polymorphic binding of the C1 domain to two positions (front and side) on the thin filament. The C1 Ig-like domain binds to the thin filament in multiple positions. (A and B) C1 is shown binding to the front of the thin filament (A) and to the side of the thin filament (B). C1 displaces tropomyosin from its closed position on F-actin when bound in the front mode and traps tropomyosin in its open state when bound to the thin filament in the side mode. Reconstructions are shown as gray transparent surfaces. Actin molecules are shown as tan ribbons; tropomyosin (Tm) in the open state is shown as green ribbons. The crystal structure of the C1 Ig-like domain (PDB accession no. 2V6H) is shown in blue (front mode) or purple (side mode). In the side mode, C1 makes a prominent contact with tropomyosin (red arrows). All complexes were formed at low Ca2+ (pCa > 8). A and B modified from Harris et al. (2016) with permission from Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. (C) Higher-resolution 3-D reconstruction showing the interface of C1 on the thin filament when bound in the side mode and interacting with tropomyosin. Highlighted region shows a 4-amino acid loop (RASK) of C1 that contacts tropomyosin and traps it in the open position. C modified from Risi et al. (2018) with permission from Structure.