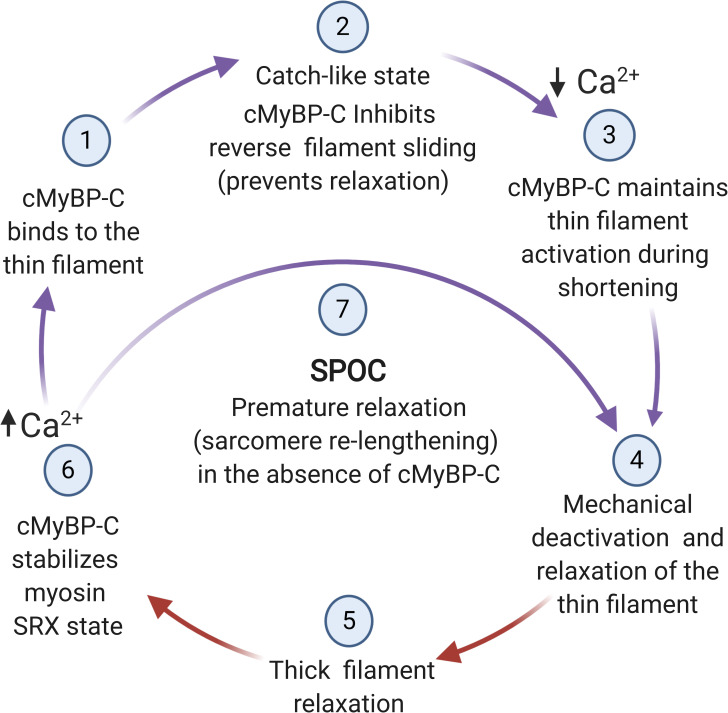
Figure 7.
Hypothetical scheme showing proposed alternating interactions of cMyBP-C with thin and thick filaments regulated by Ca2+ and mechanical signaling. (1) MyBP-C N-terminal domains undergo Ca2+-dependent binding to the thin filament and/or become repositioned on the thin filament in response to Ca2+. (2) Ca2+-activated contraction induces sarcomere shortening, whereas MyBP-C prevents sarcomere relengthening but not shortening. (3) As shortening proceeds, MyBP-C N-terminal domains maintain thin filament activation by shifting tropomyosin toward its on state. (4) Sarcomere relaxation and relengthening occurs when [Ca2+] falls below a threshold value and when mechanical control of relaxation causes MyBP-C N-terminal domains to unbind or become repositioned on the thin filament. (5) MyBP-C interactions with myosin filament promote relaxation. (6) MyBP-C stabilizes the SRX state by promoting the interacting head conformation of myosin under conditions of low load. (7) In the absence of MyBP-C, relaxation occurs prematurely because sarcomere relengthening is not prevented by MyBP-C and the activating effects of N-terminal domains are absent. Steps in the cycle where cMyBP-C N-terminal domains interact with actin are indicated by purple arrows; interactions with myosin are indicated by red arrows. Figure created with BioRender.com.