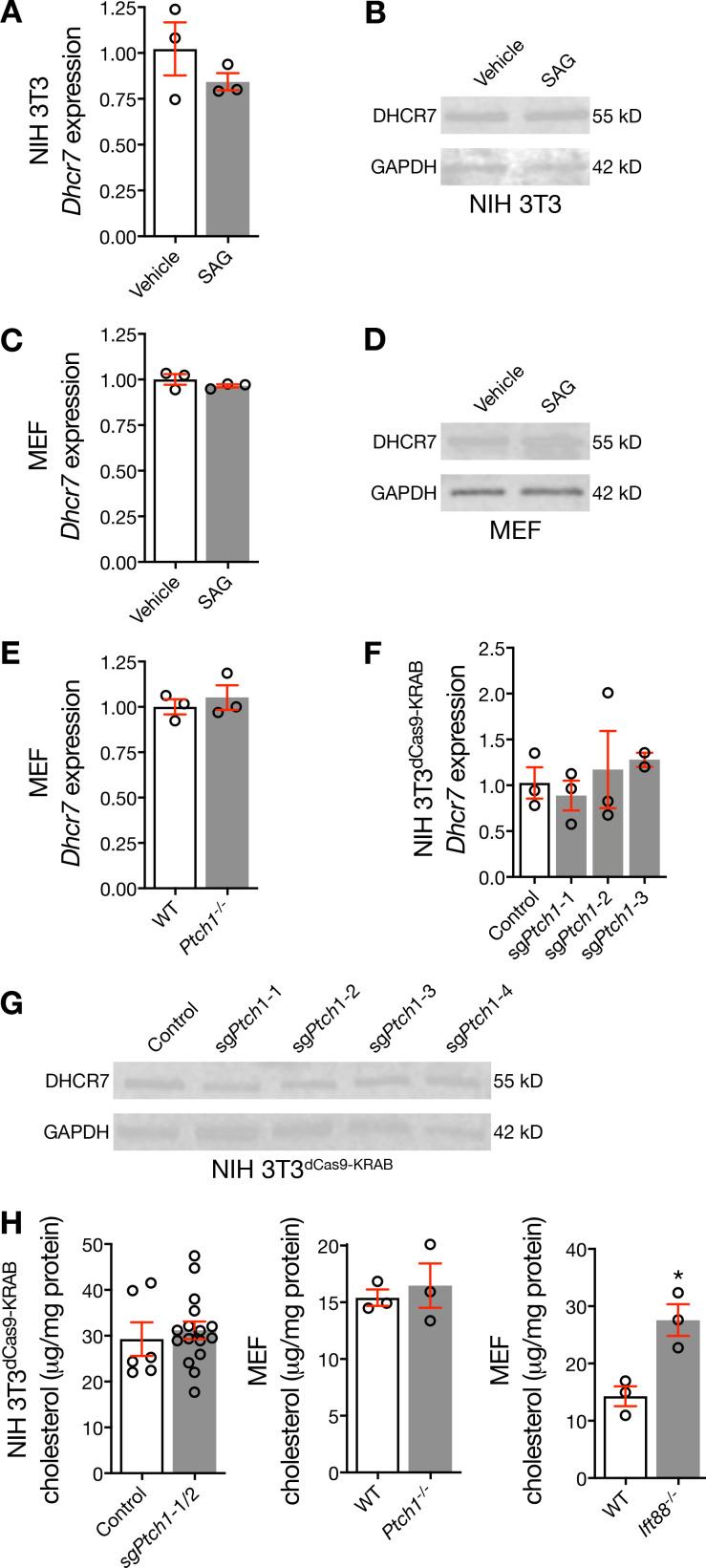
Figure S2.
Hedgehog pathway activation does not influence DHCR7 expression. (A and B) qRT-PCR and immunoblot assessment of NIH 3T3 cells demonstrates that pharmacologic activation of the Hedgehog pathway fails to alter expression of Dhcr7 or DHCR7. (C and D) qRT-PCR and immunoblot assessment of MEFs demonstrates that pharmacologic activation of the Hedgehog pathway fails to alter expression of Dhcr7 or DHCR7. (E) qRT-PCR assessment of WT and Ptch1−/− MEFs demonstrates that genetic de-repression of the Hedgehog pathway fails to alter expression of Dhcr7. (F and G) qRT-PCR and immunoblot assessment of NIH 3T3dCas9-KRAB cells transduced with sgPtch1 validates that genetic de-repression of the Hedgehog pathway fails to alter expression of Dhcr7 or DHCR7. (H) Mass spectrometry–based sterolomics of NIH 3T3dCas9-KRAB cells and MEFs show that genetic inhibition of Ptch1 does not alter levels of cellular cholesterol, but genetic deletion of Ift88 increases levels of cellular cholesterol (Student’s t test). *, P ≤ 0.05. Error bars represent SEM. The sample size of each experiment is represented by the number of independent data points on each graph. Each experiment is representative of at least three independent biological replicates.