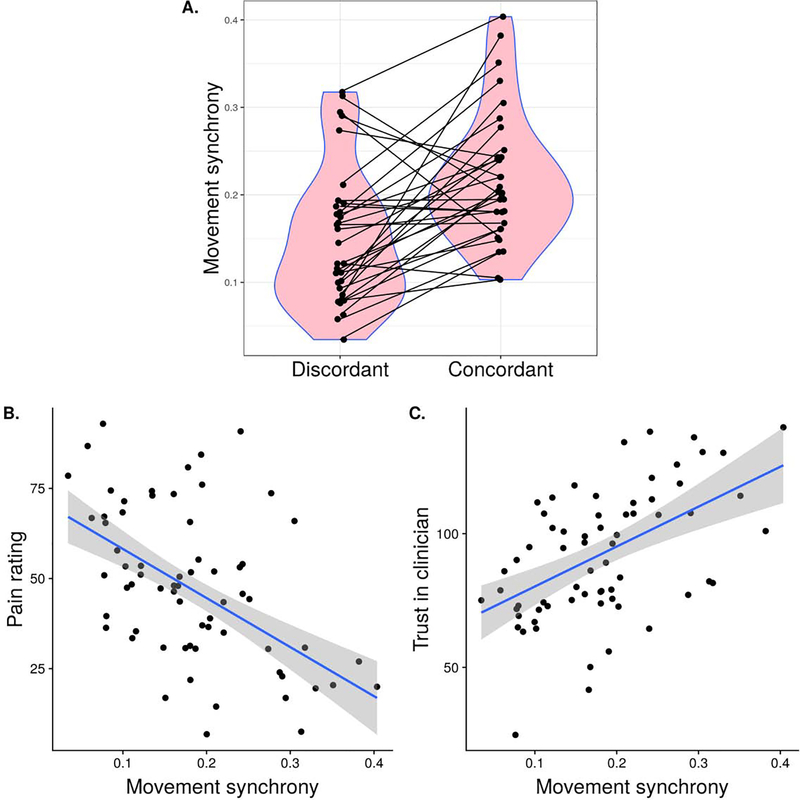
Figure 4.
(A) Movement synchrony differences between concordant and discordant dyads, based on the experimental manipulation of their perceived belief similarity (Cohen’s d=0.71). (B) Movement synchrony is negatively associated with patients’ pain ratings (Cohen’s d=0.49). (C) Movement synchrony is positively associated with patients’ trust toward the clinician Cohen’s d=0.45. Model prediction lines with corresponding 95% confidence intervals are presented.