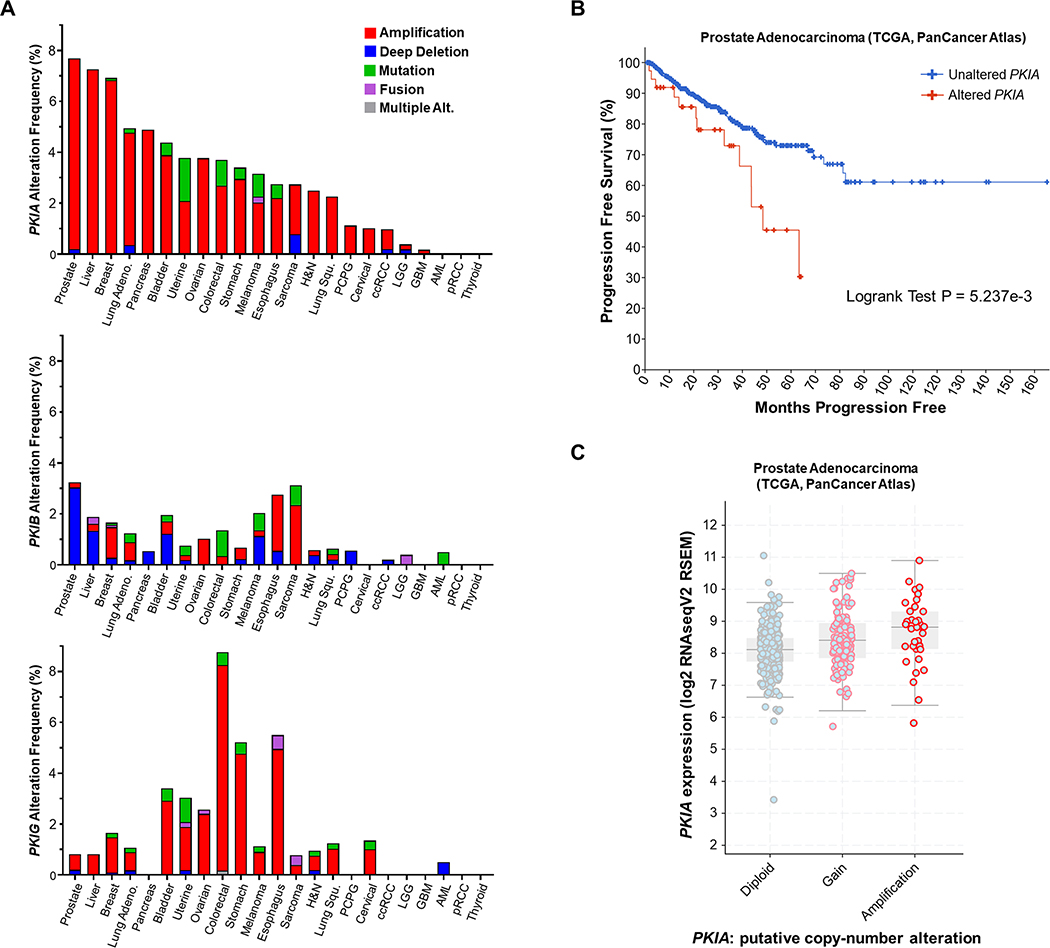
Fig. 6: PKI genomic alterations are frequent in cancer and PKIA amplification is associated with aggressive prostate cancer.
A. TCGA PanCancer Atlas analysis of PKIA, PKIB, and PKIG gene alteration frequencies in human cancers. Cancer type (X-axis) is ordered by most common PKIA gene alteration frequency. B. cBioPortal analysis of the TCGA prostate adenocarcinoma PanCancer Atlas dataset for progression-free survival (months) between patients with PKIA gene alterations vs. those with unaltered PKIA. Significance (LogRank test and exact P value) calculated in cBioPortal. C. cBioPortal Log2 RNAseq analysis of PKIA mRNA expression vs. copy-number alteration of samples in the TCGA PanCancer Atlas prostate adenocarcinoma dataset.