Fig. 7. Channel proteins persist in a spoIVB mutant and the ATP concentration remains low in both compartments.
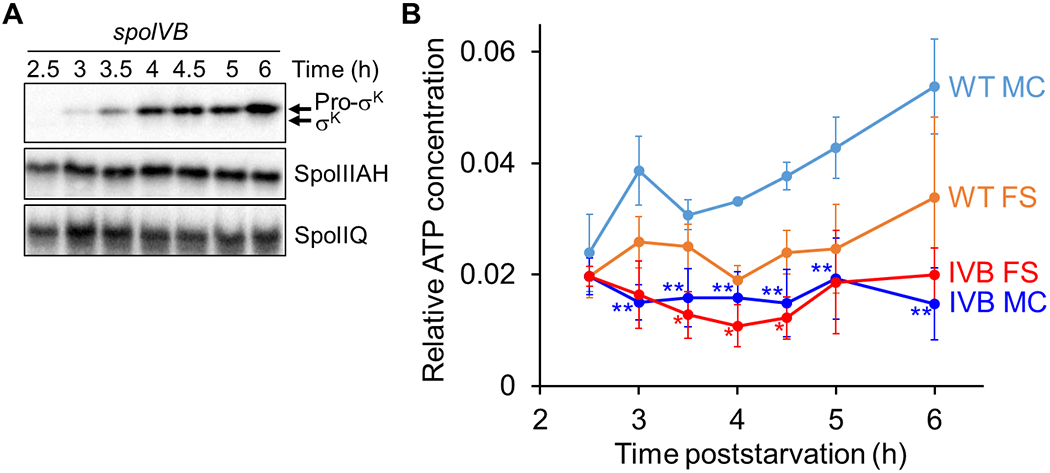
B. subtilis strains unable to produce SpoIVB and engineered to produce Luc H245F in the MC or FS were starved to induce sporulation. At 2 h PS, culture aliquots were transferred to a 96-well plate, and at the indicated times PS the luminescence intensity was measured (Fig. S7) and the Luc H245F level was assessed by immunoblot analysis with anti-Luc antibodies (Fig. S8). Samples were also subjected to immunoblot analysis using antibodies against Pro-σK, SpoIIIAH, and SpoIIQ. (A) Protein levels during sporulation. Representative immunoblots are shown for the indicated proteins. Similar results were observed for at least two biological replicates of strains expressing Luc H245F in the MC or FS. (B) Relative ATP concentration in each compartment during sporulation. For each biological replicate, the luminescence intensity was divided by the Luc H245F level to yield a normalized value representing the relative ATP concentration in the MC or the FS as indicated. Graphs show the average of three biological replicates and error bars represent one standard deviation. WT cell results are shown for comparison (same data as Fig. 3D). One asterisk (*) indicates P < 0.05 and two asterisks (**) indicate P < 0.005 in Student’s two-tailed t-tests comparing the data for each mutant with WT cells at the same time PS and in the same compartment.
