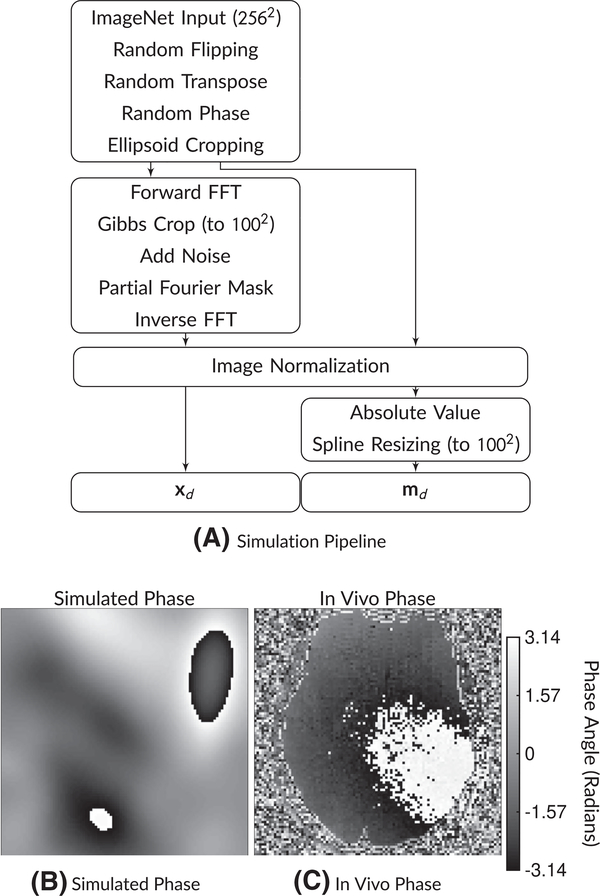
FIGURE 1.
A, Simulation pipeline and (B,C) example phase maps. The simulation pipeline begins with a 256 × 256 ImageNet image. Then, after random flipping and transposing, random phase and random ellipsoid cropping are applied. Then, the network input xd has Gibbs ringing simulated along with noise and partial Fourier masking, followed by normalization. The target md images have the absolute value operation applied followed by spline resizing to the target image matrix size. An example of a phase map from this simulation is shown in (B), while a comparison in vivo phase map is shown in (C). Phase maps can have substantial variations that must be considered when applying partial Fourier imaging