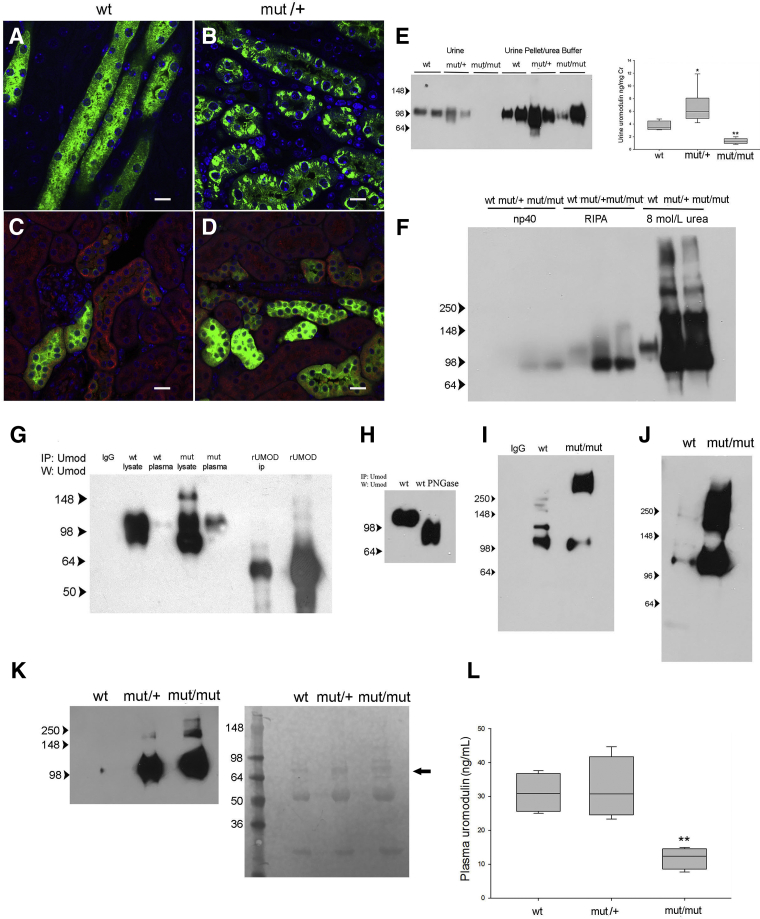
Figure 2.
A mouse model of the C106F uromodulin mutation demonstrates secretion of intracellular aggregated protein into the urine and blood. A–D: Confocal immunofluorescence images of wild-type (WT) and mutant (mut)/+ kidney sections stained for uromodulin (A and B) and uromodulin (green) and calnexin (red; C and D). E: Western blot (W) analysis for uromodulin in unprocessed urine and urine sediment solubilized in 8 mol/L urea buffer from three mouse genotypes, as indicated, and corresponding uromodulin enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). F: Western blot analysis for uromodulin in kidney lysates solubilized in buffers with increasing stringency, as indicated from three mouse genotypes. G: Western blot analysis of uromodulin using immunoprecipitates (IPs) of kidney lysates and plasma from indicated genotypes using uromodulin-conjugated dynabeads (IgG indicates control nonspecific rabbit IgG; rUMOD IP, 100 ng recombinant uromodulin peptide IP; and rUmod, 10 ng non-IP). H: Western blot analysis of uromodulin using PNGase treated (+) and untreated (−) IP of kidney plasma from a WT mouse. I: Western blot analysis of uromodulin using IP of plasma from WT and mut/mut genotypes, as indicated. J: Western blot analysis of uromodulin using IP of plasma used in I with additional treatment with 0.1 mol/L dithiothreitol and boiling. K: Western blot analysis of uromodulin using IP of plasma filtered with 200-kDa cutoff polysulphone concentrator with corresponding Ponceau S staining of membrane of Western blot of flow-through fraction showing albumin (arrow) and IgG heavy and light chains. L: Uromodulin ELISA of plasma samples (P value for mut/mut versus WT). n = 6 samples per genotype (E); n = 6 to 7 (L). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗P < 0.01 versus wt. Scale bars = 10 μm (A–D). RIPA, radioimmunoprecipitation assay.