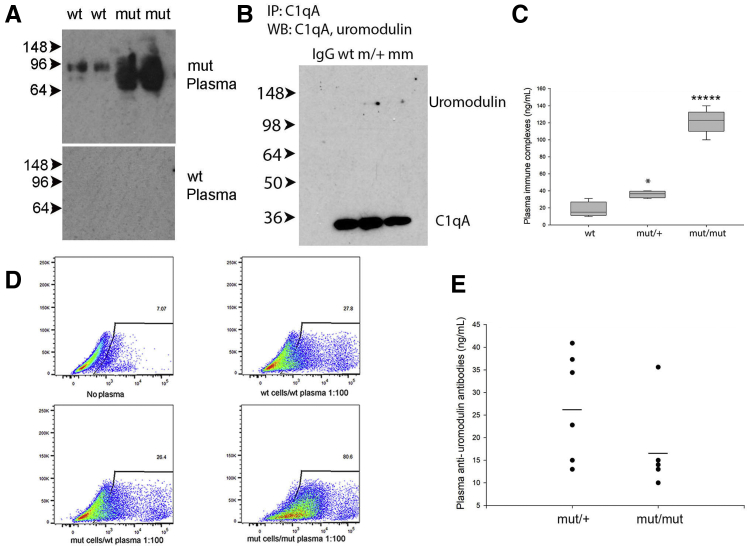
Figure 3.
C105F mutant mice produce autoantibodies against uromodulin and immune complex formation A: Western blot (WB) analysis of lysates of wild-type (WT) and mutant (mut)/+ cultured medullary tubular epithelial cells using plasma from WT and mut/mut mice diluted 1:1000. B: Immunoprecipitation of WT and mut/+ and mut/mut plasma using anti-C1q antibodies followed by Western blot analysis with anti-uromodulin antibody. Control immunoprecipitated (IP) with rabbit IgG. C: Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) for circulating immune complexes using WT, mut/+, and mut/mut plasma. D: Flow cytometry analysis of cultured WT and mut/+ medullary tubular epithelial incubated with plasma from WT and mut/+ mice diluted 1:1000. Control cells were incubated with purified mouse IgG. E: ELISA for anti-uromodulin antibodies using plates coated with recombinant mouse uromodulin amino acid 25 to 588 at 2 μg/mL and plasma from WT, mut/+, and mut/mut mice diluted 1:100. WT plasma was identical to background controls, and levels are not shown. Data are expressed as means ± SD (C and E). n = 7 per genotype (C); n = 8 per genotype (E). ∗P < 0.05, ∗∗∗∗∗P < 0.00001 versus wt.