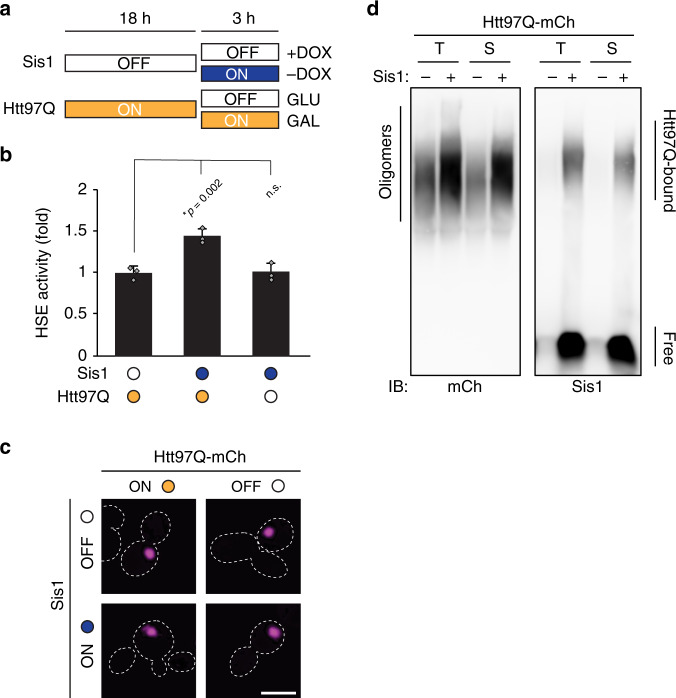
Fig. 4. Sis1 acts on soluble polyQ oligomers.
a Experimental scheme for sequential expression of Htt97Q and Sis1. Htt97Q aggregates were allowed to form in the absence of Sis1 overexpression (OFF; white) for ~18 h. Samples were then split and subjected to continued (ON; orange) or repressed (OFF; white) Htt97Q expression (galactose or glucose mediated, respectively), and to normal (OFF; white) or overexpressed levels (ON; blue) of Sis1 (doxycycline mediated), for the final 3 h before harvesting and analysis. b Ongoing Htt97Q expression is required for Sis1 dependent HSR activation. PHSELacZ activities were measured in strains treated as in a. Htt97Q aggregates were allowed to form in cells by expressing Htt97Q for ~18 h. Htt97Q expression was then continued or repressed for 3 h without or with Sis1 overexpression (orange/empty and orange/blue dots, respectively). In a third reaction, Htt97Q expression was stopped by addition of glucose and Sis1 overexpressed for 3 h (empty/blue dots). Experiments were performed in triplicate. Data represent mean + SD from three independent experiments. *p values were determined by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons t-test to Sis1 OFF control. n.s. not statistically significant. c Transient Sis1 overexpression does not remodel preexisting polyQ aggregates. Confocal microscopy was performed on cells during the conditions described in a. Scale bar = 5 μm. Experiments were performed in triplicate, representative images shown. d Overexpression of Sis1 increases the level of soluble polyQ oligomers. Total (T) or soluble (S) lysates from cells expressing Htt97Q with or without Sis1 overexpression (as in Fig. 3c) were treated with 2% SDS and analyzed by SDD-AGE (See “Methods” section for details). Immunoblotting was performed for mCherry (Htt97Q, left) or Sis1 (right). Representative blots of three independent experiments are shown. Also see Supplementary Fig. 4d.