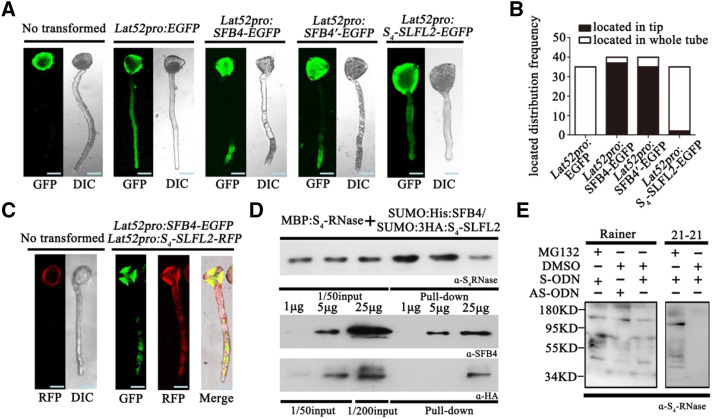
Figure 7.
The functions of SFB4 and S4-SLFL2 are distinctly different. A, SFB4, SFB4′, and S4-SLFL2 GFP fusions expressed in cv Rainer pollen tubes. Nontransformed and pollen tubes expressing empty vector were used as the control. DIC, Differential interference contrast. Bars = 10 μm. B, Number of cv Rainer pollen tubes where the proteins were located in the tip (black bars) or in the whole tube (white bars). C, Coexpression of SFB4 fused to GFP and S4-SLFL2 fused to RFP in cv Rainer pollen tubes. Bars = 10 μm. D, MBP pull-down assay to detect the interaction between MBP-S4-RNase and mixed SUMO-His-SFB4/SUMO-3HA-S4-SLFL2. Recombinant MBP-S4-RNase, SUMO-His-SFB4, and SUMO-3HA-S4-SLFL2 were purified from E. coli. Equal amounts of MBP-S4-RNase with 1, 5, and 25 μg of SUMO-His-SFB4 and SUMO-3HA-S4-SLFL2S4-RNase were detected by S4-RNase antibody. SFB4 was detected by SFB4 antibody, and S4-SLFL2 was detected by HA tag antibody. E, cv Rainer and cv 21-21 pollen tubes were cultured in pollen tube medium with S4-RNase in the presence and absence of MG132. After overnight incubation, pollen tube proteins were extracted, and S4-RNase antibody was used to detect the proteins. α-HA, HA tag antibody; α-S4-RNase, S4-RNase antibody; α-SFB4, SFB4 antibody.