Figure 1. Structure based drug design inspired by neo.
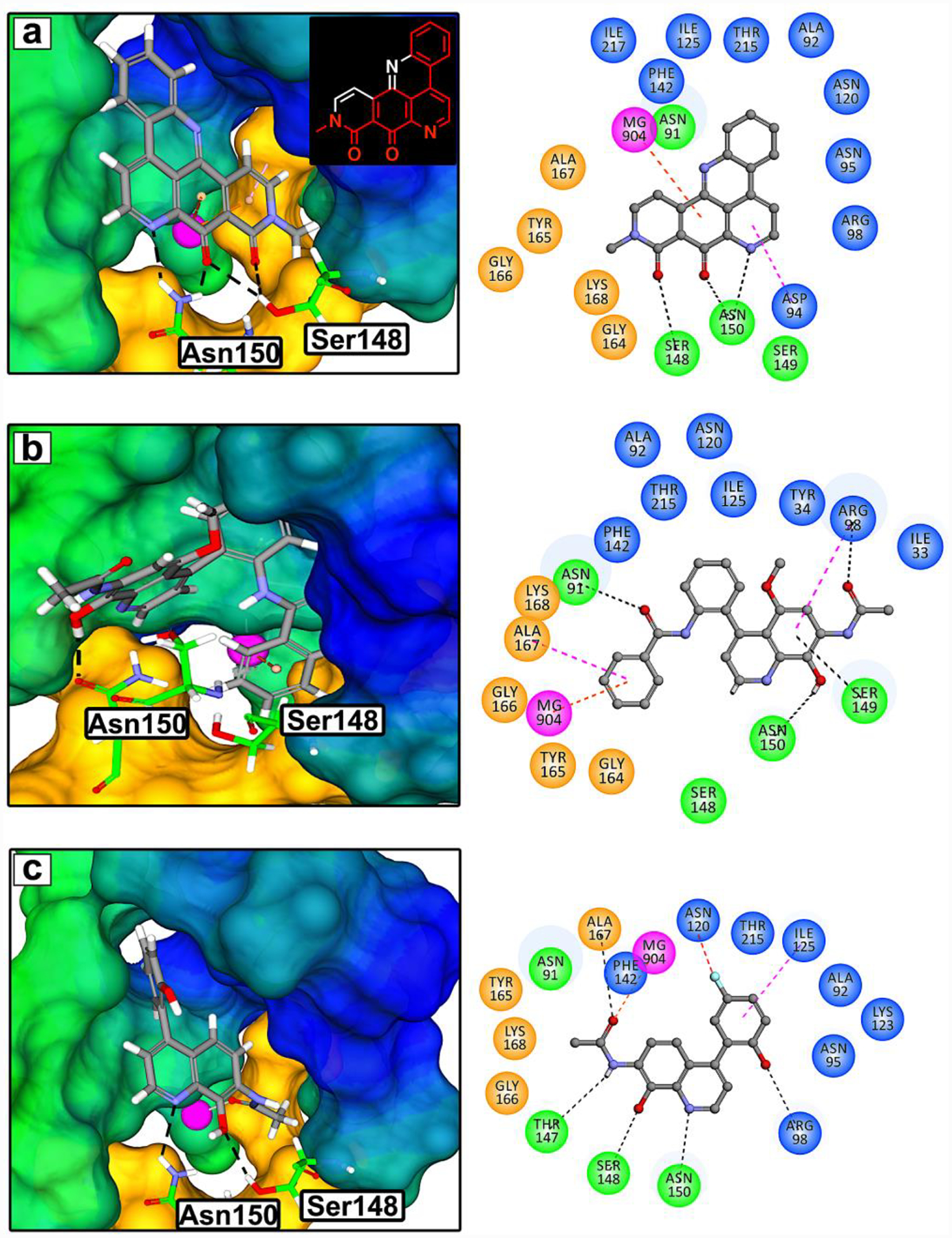
(a) 3D rendering of the molecular model of neo docked into the ATP-binding site of the N-terminal domain of TOP2A (PDB:1ZXM, 1.87Å). The colored regions represent hydrophobic (blue), hydrophilic (green), Walker A motif (orange) residues, and Mg2+ (pink sphere). Based on this model, the pharmacophore of neo was deduced to be a substituted quinoline shown as red bonds in the chemical structure. Novel TOP2A ATP-competitive inhibitor prototypes 3 (b) and 7 (c) were designed using CADD and the pharmacophore of neo. TOP2A ATP-binding site interactions are shown with a 2D rendering as dashed lines: H-bonds (black), Mg2+ π-cation or chelation (orange), π-sigma (pink), π-loan pair (blue), and halogen hydrogen bond (red).
