Figure 2.
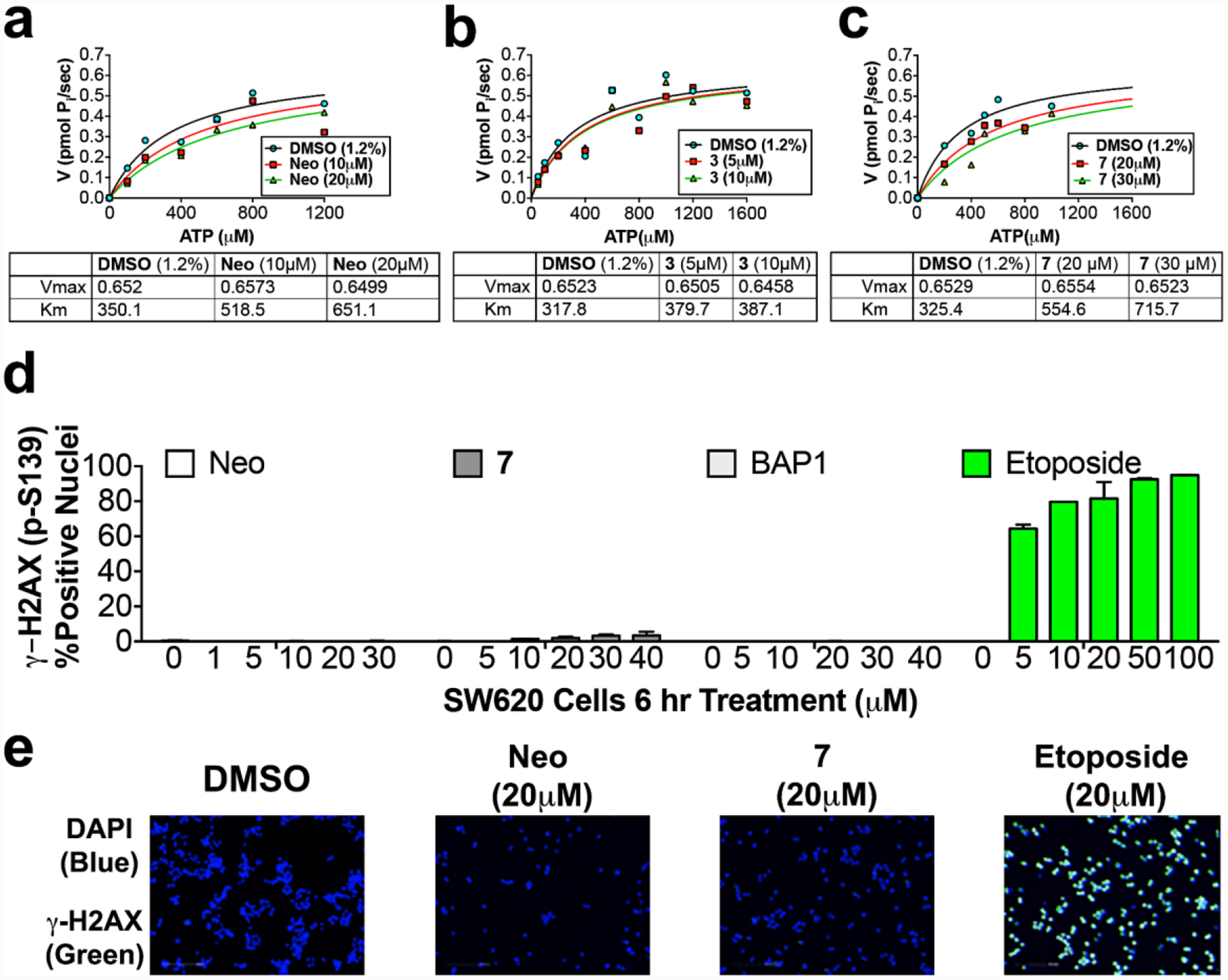
TOP2A enzyme Michaelis-Menten inhibition studies measuring ATP hydrolysis with (a) neo, (b) 3, and (c) 7. Like neo, the quinoline based pharmacophores of 3 and 7 display an ATP-competitive mode of inhibition against TOP2A, evidenced by shifts in KM with no changes in Vmax. (d) TOP2A ATP-competitive inhibitors Neo, 7, and BAP1 do not cause DNA DSBs, over a concentration range from 0–40 μM, measured by H2AX S139 phosphorylation immunofluorescence, while the TOP2A poison, etoposide, caused significant DNA damage over a concentration range from 5 to 100 μM. (e) Representative fluorescence images showing that neo and 7 do not cause induction of γ-HA2X, while etoposide caused significant induction of γ-HA2X.
