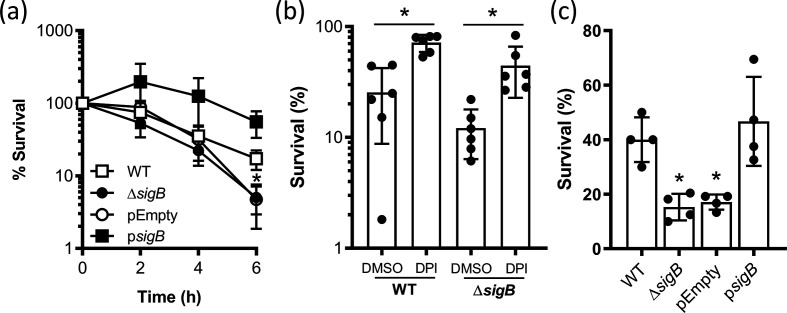
Fig. 3.
σB protects against the oxidative burst. (a) S. aureus SH1000 wild-type, ΔsigB mutant, ΔsigB mutant pEmpty and ΔsigB mutant psigB were incubated in whole human blood and survival measured by enumeration of c.f.u. at the indicated time points. Data represent the mean of six independent experiments using blood from different donors and were analysed by two-way repeated measures ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test. Data points below (*) indicate values that were significantly different from those of the wild-type (P=<0.05). (b) Survival of SH1000 wild-type (WT) or ΔsigB mutant (ΔsigB) in whole human blood containing DPI or DMSO alone (solvent control). Bars represent the mean of six independent experiments using blood from different donors. Data were analysed by two-way ANOVA with Sidak’s post-hoc test (* =<0.05). (c) Survival of S. aureus SH1000 wild-type (WT), ΔsigB mutant (ΔsigB), ΔsigB mutant pEmpty (pEmpty) and ΔsigB mutant psigB (psigB) after exposure to H2O2 for 1 h. Bars represent the mean of four independent experiments. Data were analysed by one-way ANOVA with Dunnett’s post-hoc test. *P=<0.05 relative to the wild-type. In all cases, error bars represent the standard deviation of the mean.