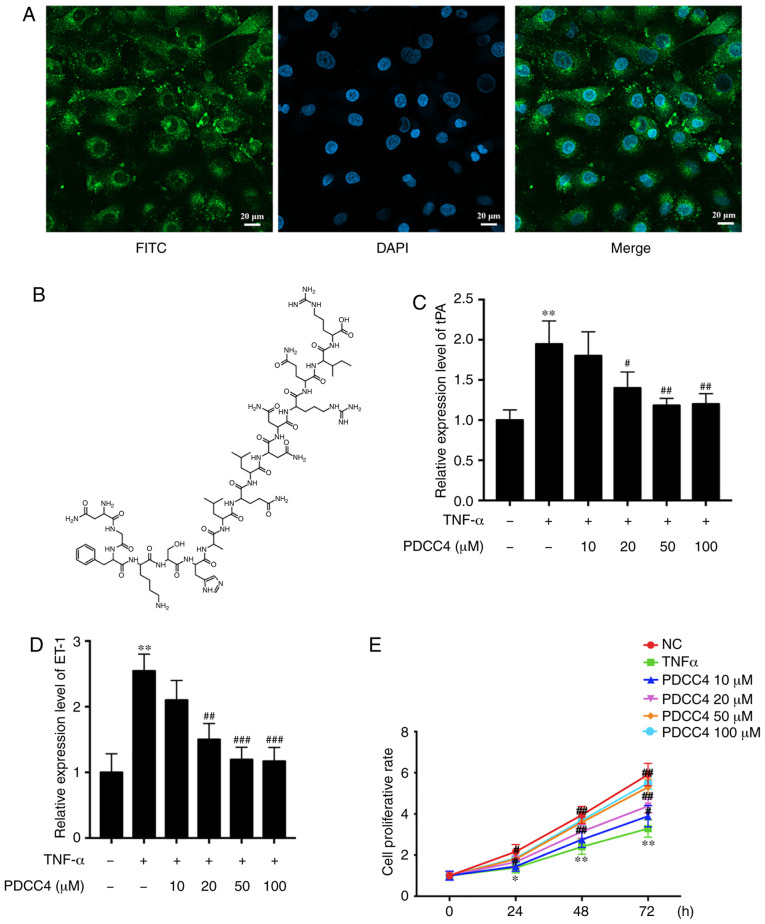
Figure 1.
PDCC4 is located in the cytoplasm and reduces the expression of markers of endothelial dysfunction induced by TNF-α. (A) Representative fluores-cent image of HUVECs after incubation with FITC-labelled PDCC4 for 1 h and staining with DAPI indicating the cell-penetrating and cytoplasm-localized properties of PDCC4. Scale bar, 20 µm. (B) Chemical formula of PDCC4. Reverse transcription-quantitative PCR indicated that PDCC4 moderated the increase in (C) tPA and (D) ET-1 expression levels induced by TNF-α in a dose-dependent manner. (E) HUVECs were stimulated with different concentrations of PDCC4 (10, 20, 50 and 100 µM) and assessed using a Cell Counting Kit-8 assay (n=3 per group). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. NC group; #P<0.05, ##P<0.01 and ###P<0.001 vs. TNF-α (+) group. HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; PDCC4, peptide derived from complement C4 A chain; ET-1, endothelin-1; tPA, tissue plasminogen activator; NC, negative control.