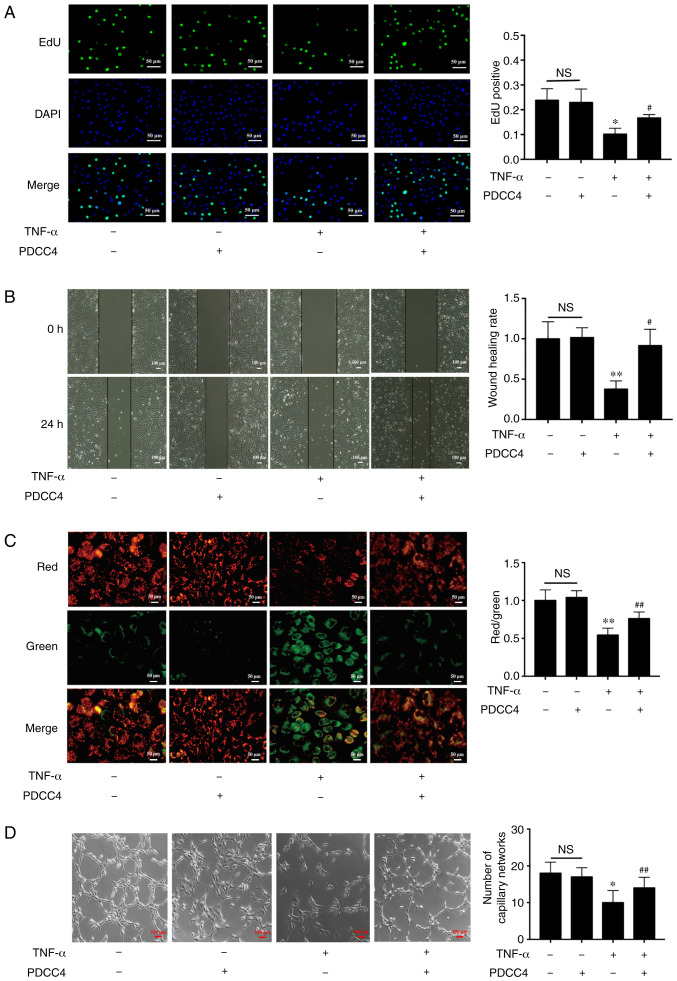
Figure 2.
PDCC4 rescues the impaired proliferation, migration, mitochondrial function and tube formation of HUVECs treated with TNF-α. (A) Proliferative HUVECs were treated with EdU, representative fluorescent images were captured and the rate of EdU labelling was calculated. The proliferation of HUVECs was inhibited by TNF-α, and this change was rescued by PDCC4 (n=3 per group). Scale bar, 50 µm. (B) Representative images of wound healing were captured at 0 and 24 h after scratching the cells, and the wound healing rate was calculated. PDCC4 prevented the migration of HUVECs from inhibition by TNF-α (n=3 per group). Scale bar, 100 µm. (C) Representative fluorescent images of HUVECs after staining with JC-1; the mitochondrial membrane potential is presented as the ratio of red to green fluorescent density. PDCC4 increased the mitochondrial membrane potential of HUVECs exposed to TNF-α (n=3 per group). Scale bar, 50 µm. (D) Representative images of the tube formation assays indicated that PDCC4 preserved the HUVEC tube formation capacity, which was impaired by TNF-α (n=3 per group). Scale bar, 100 µm. *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 vs. negative control group; #P<0.05 and ##P<0.01 vs. TNF-α (+) group. HUVEC, human umbilical vein endothelial cells; PDCC4, peptide derived from complement C4 A chain; EdU, 5-ethynyl-2′-deoxyuridine; NS, not significant.