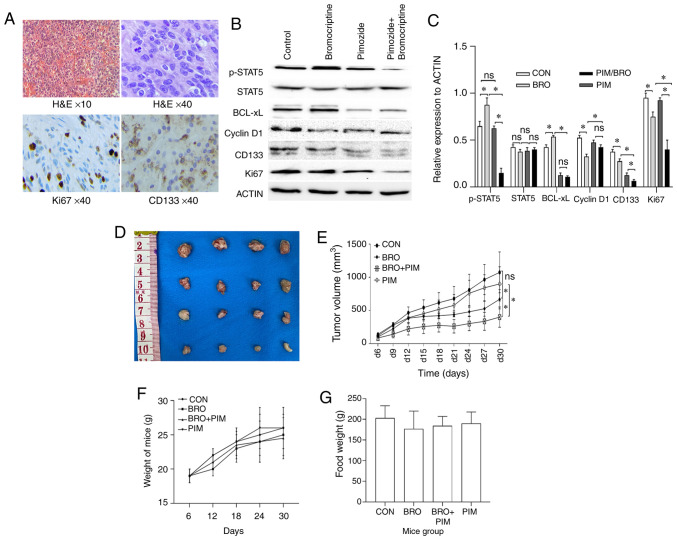
Figure 5.
(A) Representative images of H&E and immunohistochemistry staining of CD133 and Ki67 in human prolactinoma tissue xenograft tumors (magnification, ×40). Decreased CD133 and Ki67 protein expression levels were observed in the bromocriptine/pimozide group tumors. (B) Representative western blot images and (C) quantification of p-STAT5, STAT5, Bcl-xL, cyclin D1, CD133 and Ki67 protein expression levels in human prolactinoma tissue xeno-grafts. Pimozide in combination with bromocriptine suppressed the expression of tumor stem cell marker proteins CD133, compared with either drug alone. (D) and (E) Synergistic inhibitory effect of bromocriptine and pimozide on tumor growth in nude mice. Human prolactinoma tissue xenograft mice were treated daily with 20 mg/kg bromocriptine in the absence or presence of 200 µg/mouse pimozide every three days (n=3 per group). Pimozide combined with bromocriptine significantly suppressed xenograft growth. Tumor volumes were measured using calipers every other day. The tumor volume was calculated as follows: 0.5 × length × width2. Results are presented as the mean ± standard error of the mean. *P<0.05. (F) Body weight change and (G) food intake in mice during the experimental period. Data are presented as the mean ± SD. Statistical significance was calculated using t-test. H&E, hematoxylin and eosin; p-, phospho-; STAT5, signal transducer and activator of transcription 5A; Bcl-xL, B-cell lymphoma extra-large; si, small interfering; CON, control; BRO, bromocriptine; PIM, pimozide; ns, not significant.