Fig. 3.
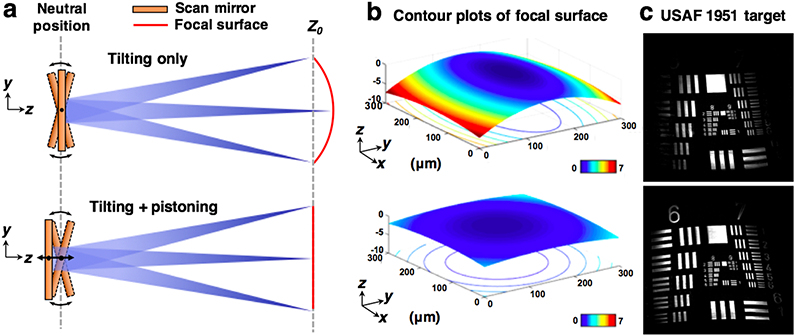
Concept and characterization of MEMS pistoning for flat-field correction. (a) A simplified diagram of the scan head, showing that axial pistoning of the MEMS scanner can counteract the curvature induced by the tilting motion. (b) A contour plot of the focal surface (at the FFP of the objective) showing that the uncorrected field curvature along the y-axis (scan direction) of the FOV is > 7 μm in axial extent, but is reduced to < 2 μm after flat-field correction (which is comparable to the axial resolution of the system). (c) Images of a flat resolution target showing that more of the target is in focus after the flat-field method is applied.
