Figure 2.
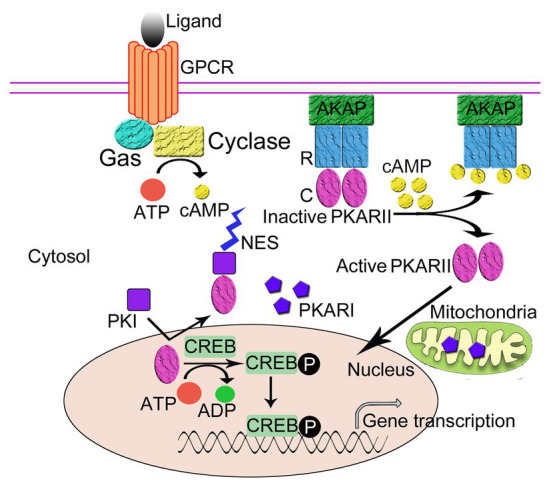
The regulation of the intracellular localization of PKA. The regulatory subunits (R) of PKA bind to A-Kinase Anchoring Proteins (AKAPs), which anchor the PKA holoenzyme to the plasma membrane thus regulates the intracellular localization of PKA. Protein kinase inhibitor peptide (PKI) also regulates the intracellular localization of PKA. Following activation by cAMP, the R subunits of PKA dissociate from the catalytic subunits (C). The C subunits diffuse into cell nucleus and phosphorylate the cAMP-response element binding protein (CREB), which can then activate gene transcription. PKI enters the nucleus and binds to the free C subunits of PKA and exposes the nuclear export signal (NES) of PKI to transport the C subunit out of the nucleus in an ATP-dependent manner thus inhibits the activity of C subunits.
