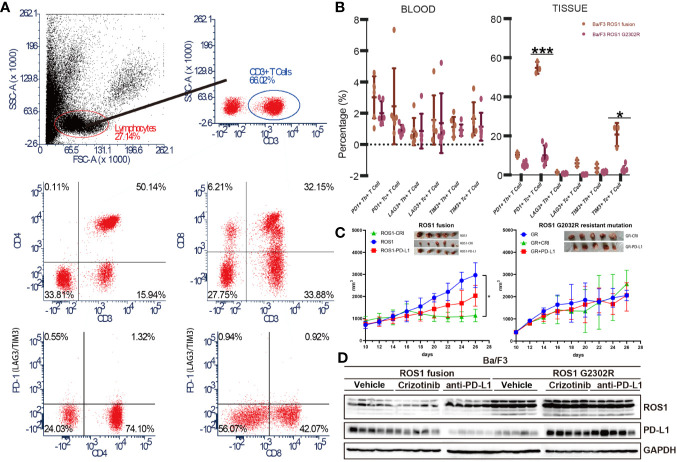
Figure 5.
Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion bearing mouse showed an increased response to ant- programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) therapy than Ba/F3 ROS1 G2032R resistant mutation. (A) Flow cytometry and analysis strategies used in this study; (B) Flow cytometric analysis of PD-1, lymphocyte activation gene 3 (LAG-3) and T-cell immunoglobulin mucin-3 (TIM3) in Ba/F3 in ROS proto-oncogene 1, receptor tyrosine kinase (ROS1) fusion and Ba/F3 ROS1 G2032R mutation of blood and tissue samples based on T cell type; (C) Tumor size changes in Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion in Ba/F3 ROS1 G2032R mutation C3H mice (n = 5) after crizotinib or anti-PD-L1 therapy. ROS1+CRI: Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion+crizotinib; ROS1: Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion; ROS1+PD-L1: Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion+anti-PD-L1; GR: Ba/F3 G2032R mutation; GR+CRI: Ba/F3 G2032R mutation+crizotinib; GR+PD-L1: Ba/F3 G2032R mutation+ anti-PD-L1; (D) Western blotting analysis of ROS1 and PD-L1 in Ba/F3 ROS1 fusion and Ba/F3 ROS1 G2032R mutation of tissue samples after crizotinib and anti-PD-L1 ICI therapy. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant and denoted as follows: *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001.