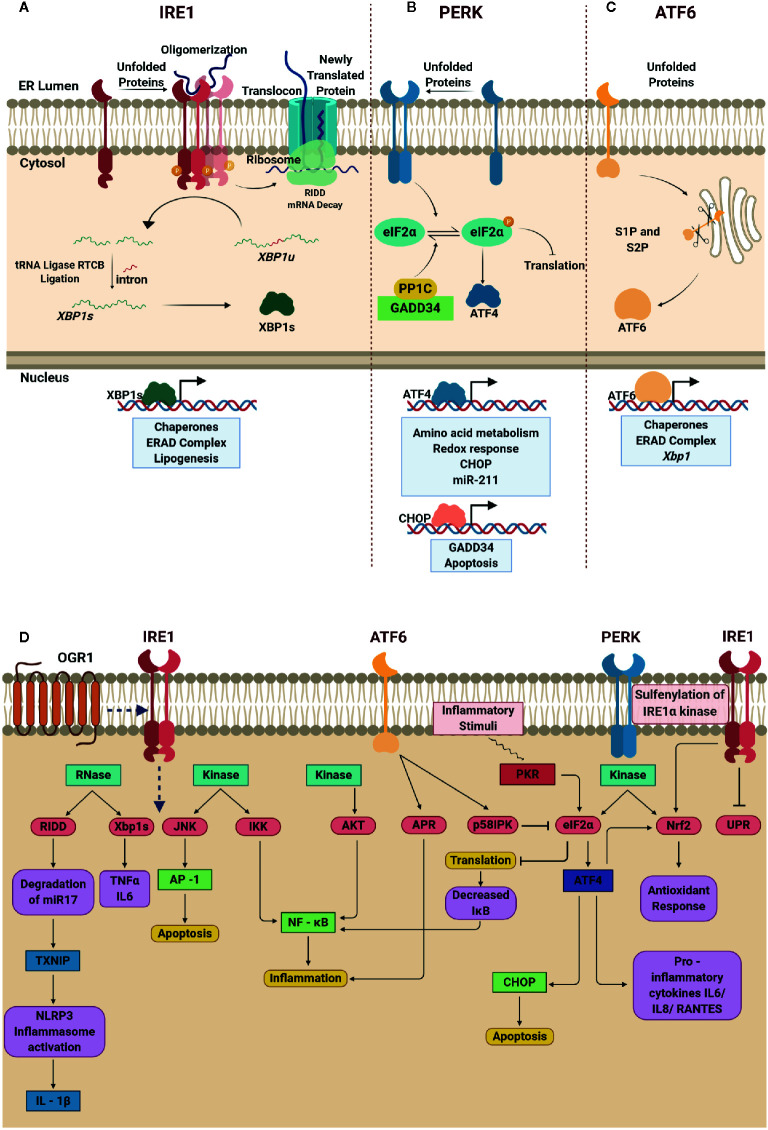
Figure 1.
Schematic depiction of unfolded protein response (UPR) signaling cascade, and the interplay between endoplasmic reticulum (ER) stress response and inflammation. (A) Oligomerization of IRE1α in the presence of unfolded proteins promotes the endoribonuclease activity of IRE1α and unconventional splicing of XBP1 generating functional XBP1 that regulates gene expression. IRE1α promotes RIDD-dependent mRNA decay and reduces protein overload in the ER lumen. (B) Activated PERK drives phosphorylation of eIF2α resulting in translational block. At this juncture, selective IRES dependent translation of ATF4 is promoted to induce chaperones and mitigate oxidative stress as well as apoptosis. (C) Dissociation of BiP from ATF6 leads to translocation of ATF6 from the ER membrane to Golgi promoting its cleavage by S1P and S2P generating functional ATF6 that regulates UPR genes. (D) In IRE1α pathway, the RNase domain is involved in Xbp1 splicing and RIDD mechanism upregulates the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNFα, IL-6 and IL-1β; the kinase domain activates JNK and IKK signaling pathway that results in apoptosis and inflammation respectively. Additionally, activation of proton-sensing OGR1 is responsible for ER-stress mediated response via IRE1α-JNK-XBP1s axis. The kinase activity of ATF6 leads to phosphorylation of AKT ensuing inflammation via NF-κB signaling. The cleaved p50ATF6α acts as a transcription factor and upregulates the expression of APR genes and ER co-chaperone p58IPK that in turn blocks the phosphorylation of eIF2α. PERK is one of the kinases that phosphorylate eIF2α at Ser 51, which enables selective translation of ATF4. ATF4 drives the expression of CHOP and pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-6, IL-8, and RANTES. Induced expression of CHOP abrogates pro-survival signaling leading to cell death. Notably, the translational block decreases further translation of IκB ensuing inflammation due to increase in NF-κB. Nrf2, another notable target phosphorylated by PERK that is known to manifest antioxidant response. Created with BioRender.com.