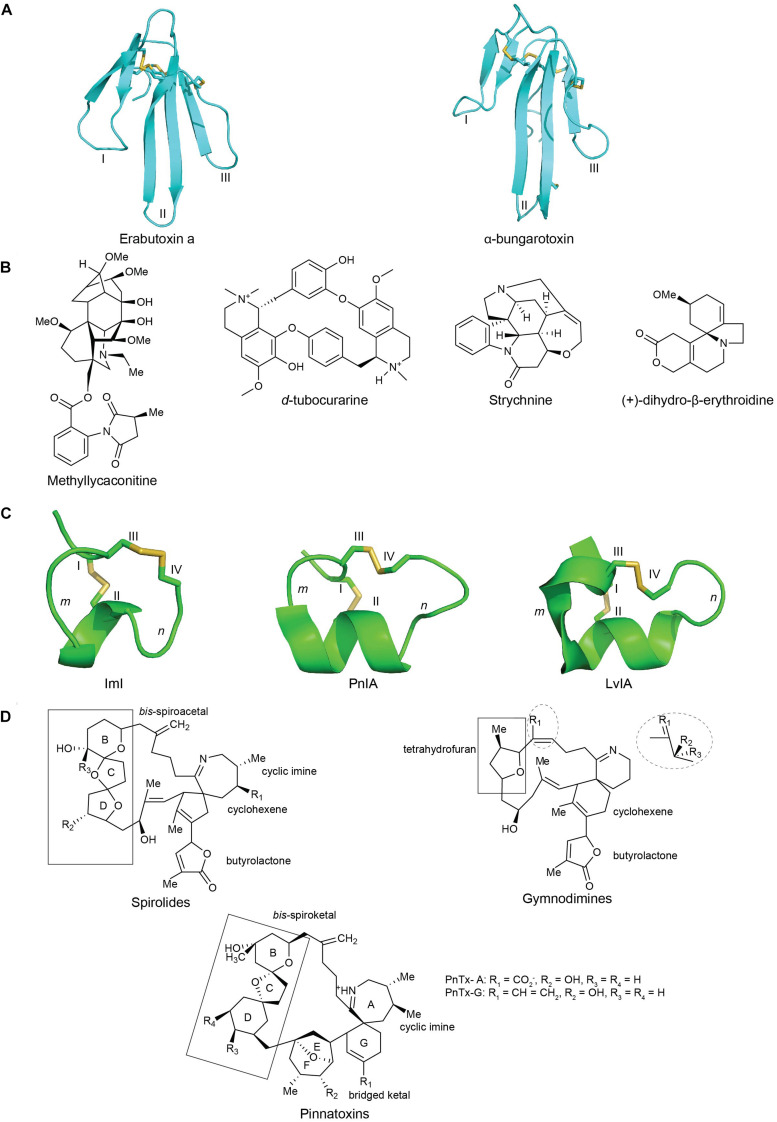
FIGURE 3.
The structures of nAChRs inhibitors from plant, snake, cone snail and dinoflagellate toxins: (A) chemical structures of plant toxins: methyllylcacotinine, d-Tubocurarine, strychnine and (+)-dihydro-β-erythroidine (DHβE) (Daly, 2005); (B) three-dimensional structure of the three-finger snake toxins with three adjacent loop (I, II, and III): short chain α-neurotoxins erabutoxin a (PDB 5EBX) (Corfield et al., 1989) and long chain α-bungarotxin (PDB 1KFH) (Moise et al., 2002); (C) three-dimensional structures of α(m/n)-conotoxins with m, n being number of residues within the two loops formed by natively disulfide bond CysI -CysIII and CysII -CysIV : ImI (PDB 1IMI) (Maslennikov et al., 1999), PnIA (PDB 1PEN) (Hu et al., 1996), and LvIA (PDB 2MDQ) (Luo et al., 2014); (D) chemical structures of spirolides, gymnodimines and pinnatoxins, reprinted from ref (Bourne et al., 2010; Otero et al., 2011; Bourne et al., 2015). Disulfide bonds in three-dimensional structures are colored in yellow.