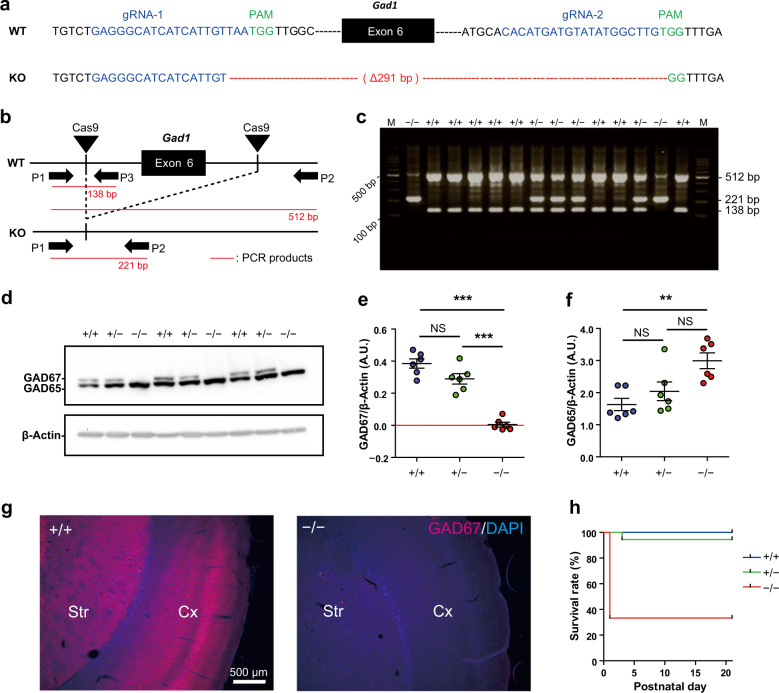
Fig. 1. Generation of Gad1 knockout rats by the CRISPR/Cas9 system.
a Targeted site of Gad1 knockout rats. WT and KO represent wild-type and knockout alleles, respectively. The two sequences highlighted in blue denote the sites recognized by the complex of Cas9 and guide RNAs (gRNA-1 and gRNA-2). The protospacer adjacent motif (PAM) sequences next to the two sites are highlighted in green. The KO allele has a 291-bp deletion, including exon-6 of the Gad1 gene. b Schematic representation of CRISPR/Cas9-mediated deletion of exon-6 and the approximate locations of primers for genotyping PCR (P1, P2, and P3). c A representative result of genotyping PCR. M: DNA molecular weight marker. d Protein levels of GAD67 in the adult brain taken from each genotype (n = 6 in each genotype). e Western blot analysis using an antibody that binds both GAD65 and GAD67 revealed the loss of GAD67 protein in Gad1−/− rats (F(2, 15) = 55.372, p < 0.001). f GAD65 was increased in Gad1−/− rats (F(2, 15) = 8.0857, p < 0.01). β-Actin was used as an internal control in d–f. g The loss of GAD67 immunoreactivity in the Gad1−/− rat was also observed in the immunohistochemical analysis. Cx cerebral cortex, Sr striatum. The nuclei were stained using DAPI. Scale bar = 500 μm. h Gad1−/− rats showed a significantly lower survival rate than Gad1+/+ and Gad1+/− rats (log-rank test, p < 0.001). The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA and post hoc test adjusted by Holm’s method for multiple comparisons (e, f) and log-rank test (h). The results are presented as the average ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001.