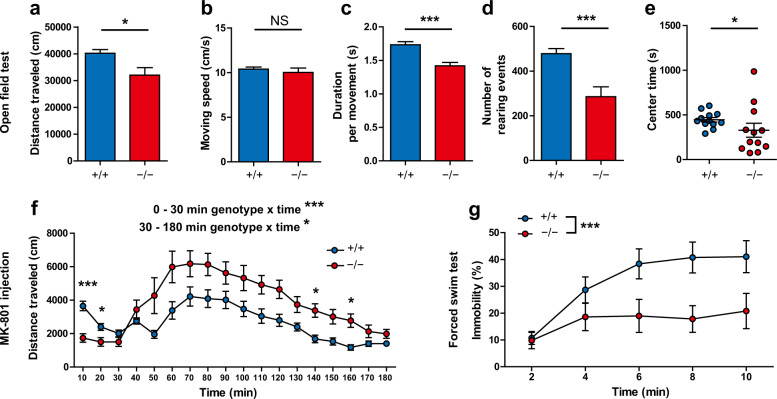
Fig. 3. Task-dependent alterations of activities in Gad1−/− rats.
a–e Open field test (n = 12 for each genotype). Gad1−/− rats exhibited decreased distance traveled compared with Gad1+/+ (t(16.051) = –2.6272, p < 0.05) (a), but their moving speed was unaltered (t(15.717) = −0.6772, p = 0.5081) (b). Duration per movement (t(21.82) = –4.541, p < 0.001) (c) and number of rearing events (t(16.456) = −3.8561, p < 0.01) (d) were also decreased in Gad1−/− rats, suggesting hypoactivity in the open field. Gad1−/− rats stayed less time in the center region (W = 37, p < 0.05) (e). f Response to NMDA receptor antagonist (Gad1+/+, n = 12; Gad1−/−, n = 11). Gad1−/− rats showed hypoactivity at baseline (0–30 min; genotype × time, F(2, 40) = 9.3185, p < 0.001) but showed enhanced hyperactivity after MK-801 injection (0.2 mg/kg, intraperitoneal injection) (30–180 min; genotype × time, F(14, 280) = 1.9404, p < 0.05; simple main effect of genotype, adjusted by Holm’s method for multiple comparisons; 130–140 min, p < 0.05; 150–160 min, p < 0.05). g Forced swim test (Gad1+/+, n = 12; Gad1−/−, n = 11). Gad1−/− rats showed a significant decrease in immobility (genotype main effect, F(1, 20) = 6.4689, p < 0.05). The results are presented as the average ± SEM. The data were analyzed using the Wilcoxon rank-sum test (e), two-way repeated measures ANOVA (f–h), and Welch’s t-test (others). *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001; NS not significant.